Straight table
The Straight table shows several fields simultaneously, where the content of each row is logically connected. A table can consist of as many dimensions and measures as needed.
App creators can add many fields simultaneously, customize the table at the column level, add alternative dimensions and measures, set column width, apply pagination, and turn on chart exploration.
The straight table offers flexible, accessible, and responsive data analysis, including the following features:
-
Ease of use: One-click interactive sorting and ability to drag and drop columns to reorder them without affecting chart defaults or sorting preferences.
-
Flexible configuration: Application developers can use options for pagination, keyboard navigation, screen reader support, and enhanced readability. Accessibility enhancements can be switched off if needed to add more mouse shortcuts into column headers.
-
To learn more, see Managing accessibility settings.
-
-
Options for row-level pagination, comprehensive keyboard navigation, screen reader support, and enhanced readability.
-
Optimized performance for large data volumes.
-
Chart exploration allows users that do not have edit rights to customize the original straight table when they are in analysis mode. These users can add or remove columns, change sort order, re-arrange columns, and make selections. They can then share, download, subscribe, or bookmark the new table layout. The changes made in chart exploration mode by a user are not seen by other users analyzing the sheet.
When to use the straight table
Use a straight table when you want to view detailed data and precise values rather than visualizations of values. Tables are good when you want to compare individual values. Drill-down group dimensions are very efficient in tables. Within a limited space, you can drill down to the next level of detail and analyze the updated measure values. Use this table when you want users to be able to create custom tables in analysis mode.
Advantages
You can filter and sort the table in different ways. Many values can be included in a table, and when you drill down in a table, you make good use of the limited space on the sheet. A table is excellent when you want to see exact values rather than trends or patterns. Tables are an easy way to export data into other programs.
Disadvantages
If the straight table contains many values, it is difficult to get an overview of how values are related. It is also hard to identify an irregularity within the table.
Best practices for optimizing tables
If a table has too many dimensions and measures, it may load slowly. As a best practice, add the majority of your fields and expressions as Alternative columns. This encourages users to add only the fields they need using chart exploration.
You can also increase performance by ensuring a table has 10 columns or less.
Tables that extract fields from a single data source will perform better than tables that contain fields from multiple data sources.
Selecting active fields from cyclic dimensions in straight tables
If a straight table uses a cyclic dimension, analyzers can select the active field from the cyclic dimension.
Do one of the following, depending on chart accessibility settings:
-
Click
next to the column name, and select the dimension.
-
Click
on a cyclic dimension column, and then click
<Dimension name> and select a dimension from the cyclic dimension.
Using chart exploration
Chart exploration mode is a great way to quickly remove or add data, and then share it, download it, or bookmark the new table state. It is available in the menu under
Chart exploration. Your app creator needs to turn this setting on for you to use it.
You use chart exploration in analysis mode. Add or remove columns from a table, re-sort columns, change column width, and apply selections. You cannot change the size or layout of the entire table on the sheet in chart exploration mode.
If you customize a table using chart exploration mode, other users cannot see your changes, unless you save them as a public bookmark. This means that several users can alter the same table, at the same time. Your changes will remain visible to you until your session ends. When this occurs, the table will return to its default state, as set by the person who created the straight table. If you want to save your table layout, create a bookmark. For more information, see Creating bookmarks.
The chart exploration panel is not shown in the resulting table that you have shared or downloaded.
For information about configuring chart exploration as an app creator, see Activating chart exploration in a straight table.
Chart exploration of a straight table. The table has three columns: Customer, Region, City.
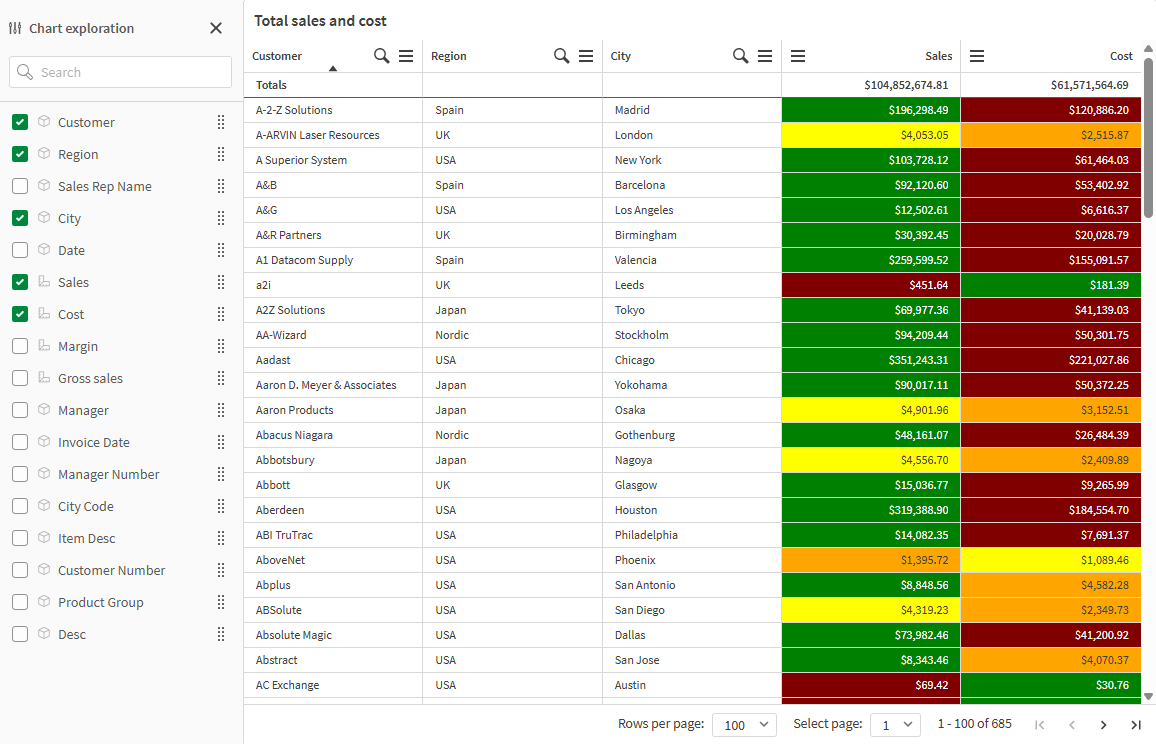
Chart exploration of the same table as above, but with two measures added to the table: Sales and Cost. The background colors are the result of an expression.
Downloading a straight table as data
When you download a straight table as data, you can choose to include the following in the downloaded Excel file:
-
Titles, subtitles, and footnotes
-
Column totals
-
Current selections
Do the following:
-
In the hover menu, click
Download.
You can also click
>
Download.
- Select Data.
- Under Export options, select the additional content you would like to include. Depending on the configuration of your chart, one or more of the following options might be available:
- Titles: Include titles, subtitles, and footnotes.
- Column totals: Include the row displaying totals at the top or bottom of the table.
- Current selections: Include a list of selections applied in the app at the time when you download the table. A separate row is added for each field that has selections.
- Click Download.
Straight tables can also be downloaded as images and PDFs, using the same workflow as for other charts. For more information, see Downloading visualizations.
Limitations
Chart exploration limitations
Chart exploration for straight tables added to containers
Chart exploration is not available if the table is embedded inside any of the following objects:
-
An existing container object that has not been replaced with a tab container. The tab container became the native container object on November 5, 2024.
Chart exploration is also not available in existing instances of the deprecated ShowHide container and Tabbed container objects. However, converting these objects to tab containers is not recommended. Instead, create a new tab container from scratch in order to access chart exploration in straight tables.
For information about the former native container object, see Container
For information about the tab container, see Tab container.
-
Trellis container
Chart exploration for straight tables embedded in web pages
Chart exploration is not available for straight tables that are embedded in web pages.
Number of rows displayed
If pagination is turned on, you can only display 100 rows at a time. If pagination is turned off, you can display up to 250 000 rows at a time. If your table has more than 250 000 rows, pagination will be applied.
Because huge tables are impractical and hard to manage, the limit for what is practical is far less than the theoretical maximum. In most cases, it is desirable to see all the columns without scrolling horizontally.
Accessibility
The straight table is only fully accessible with certain settings activated. For more information, see Managing accessibility settings.
For more information on keyboard navigation, see Keyboard navigation and shortcuts in apps.
