The box plot is suitable for comparing range and distribution for groups of numerical data, illustrated by a box with whiskers, and a center line in the middle. The whiskers represent high and low reference values for excluding outlier values.

You can define the box start and end points, and whiskers ranges with a few different presets, or define your own settings using expressions.
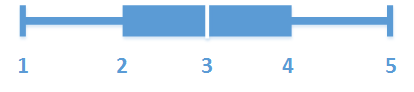
- First whisker
- Box start
- Center line
- Box end
- Last whisker
When to use the box plot
The box plot is suitable for comparing range and distribution for groups of numerical data.
Advantages: The box plot organizes large amounts of data, and visualizes outlier values.
Disadvantages: The box plot is not relevant for detailed analysis of the data as it deals with a summary of the data distribution.
