Managing field-level metadata and data profiling
Field-level metadata lets users apply aliases, descriptions, and classifications to fields; these features assist with identifying specific data and sensitive fields.
Data administrators access rich technical information about their datasets from profiling. App developers use profile statistics and data sampling to gain ideas and direction for creating apps and planning visualizations. Field profiling can help data analysts and business users to gain insights faster. They can view and visualize valuable field profile metrics at-a-glance without needing to create an app first.
Permissions
Permissions are required to profile and sample data. You must have a role in the dataset's space that allows you to profile data sources. For more information, see Managing permissions in shared spaces or Managing permissions in managed spaces.
Managing field-level metadata
You can access and edit metadata for every field in your dataset from the Profile tab.
Select any card from the 

Data view to open that field's Details panel to the right of the grid. Field-level metadata fields — Field alias, Description, Tags, and Classification— are optional and can be defined and edited from this panel.
| Detail | Description |
|---|---|
| Field alias | Enter an optional alternate name to make field names more meaningful in the profile analysis. Alias field names only display in the profile analysis and do not impact technical column names. |
| Description |
Enter any information that may be helpful to users viewing field metadata and profiling for the field. |
| Tags | Enter text snippets to define and categorize this field and its data. |
| Classification | Select the checkbox for Personal information or Sensitive information. |
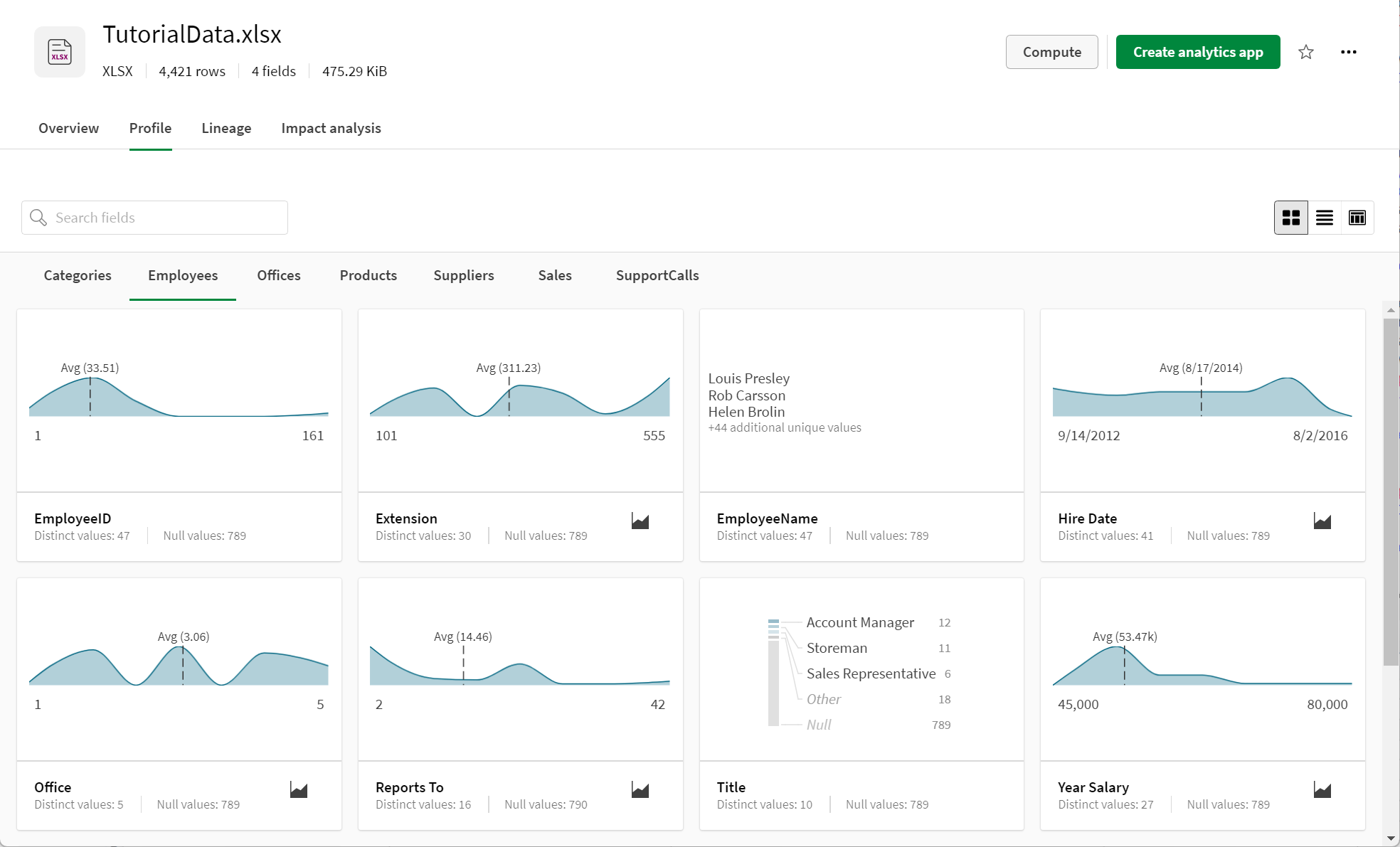
Field-level metadata for an XLSX file with multiple sheets
Not all data types are profiled by default. The following instead display a limited profile until you profile them:
-
QVD
-
Parquet
For more information on the limited profile, see Limited profile view
Profiling data
Profile statistics provide column analyses that measure incidence, ranges, and values that occur within datasets. These metrics describe relationships between field values such as:
- Count of distinct values (cardinality)
- Sample values, most common values, and value frequency
- Redundancies useful in identifying default or potential duplicate values
- Counts of null, string, and numeric values
- Information about value ranges including min, max, average, sum, and standard deviation
Catalog provides three views of field profile data:
-
Tile view is a card-based, visual representation of fields laid out as a grid.
-
List view is a tabular summary of configurable profile statistics.
-
Table view lists field column names and up to the first twenty records of the dataset.
Select the Tile

icon to switch between profile views.
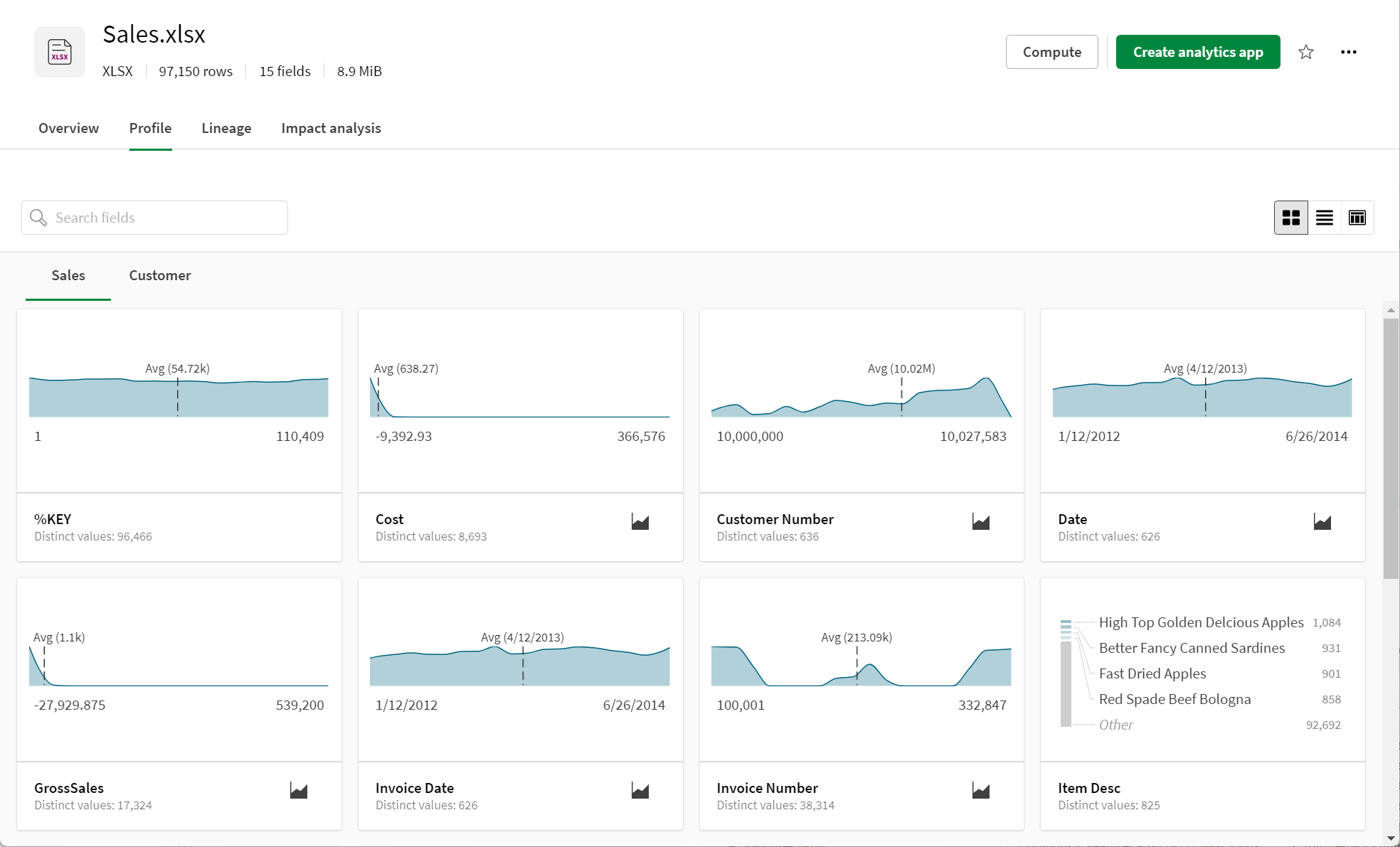
Tile view
Profile tile view is a visual field profile designed to display the most informative content for that type of field. The default view card type shown is determined by whether the number of numeric or text values is higher for that field. For example, for fields with both text and numeric values, Most Common Values card type displays by default if there are more text values and the Binned Frequency numeric distribution card type displays if there are more numeric values in the field. A dropdown toggle is provided so that you can switch over to the Most Common Values card type for any field that has non-unique values when is selected; or you can switch back to the numeric distribution card if Binned Frequency
is selected. Note that all card types include the number of null values, if the field has null values.
Tile view: Fields are profiled by metrics that are meaningful for the type of data contained in that field (for example: text versus numeric values)
Sample values card
The Sample values card is shown when all values are unique and text-only. It will list (up to) the first three values and the total number of additional unique values.
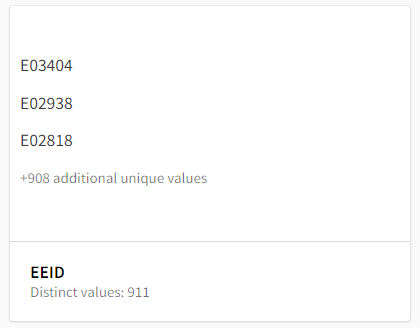
Sample values profile criteria: Field values are profiled with this card when cardinality is high (all distinct values). In a case where every value is text-based and unique, a few sample values provides the best initial view into this type of field's data.
Each Sample values profile card provides:
- Field name
- Cardinality (distinct values)
- Up to three sample values (fields may have less than three values)
Most common values frequency card
The Most common values frequency card shows the five most common values and their frequency. If there are more values than five distinct values, these are combined and displayed as Other. If any fields are missing values, the total is displayed as Null. This profile card can be applied on text, numeric, or mixed data values.
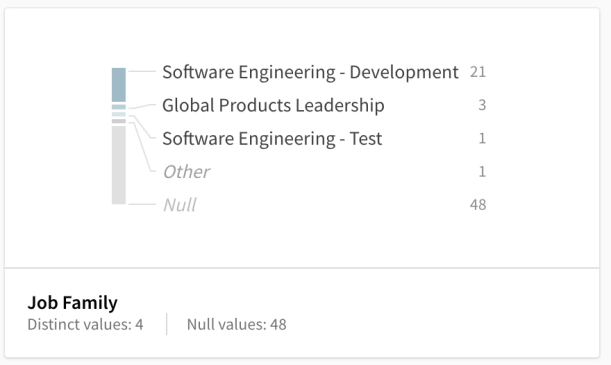
Most common values frequency criteria: Fields that have few values or a skewed distribution of values are profiled with the most common values frequency card. This profiling is only applied when there are multiple instances of the same values. Users can gain quick insight into the distribution of field values. If the field data includes both text and numeric values, and there are more text than numeric values, then the Most common values frequency card is shown. The Binned frequency toggle is provided when there are more than three numeric values in the field.
Each Most common values frequency profile card provides:
- Field name
- Cardinality (distinct values)
- Most common values and their frequency
- Other combined frequency of remaining values
Binned frequency card
The Binned frequency card shows distribution and profiling information that is relevant for numeric fields; including minimum, average, and maximum data values. If the field data includes both text and numeric values, and there are more numeric than text values, then the Binned frequency card is shown. The Most Common Values Frequency card type is available for all fields that have non-unique values.
Tile view card: Binned Frequency numeric distribution
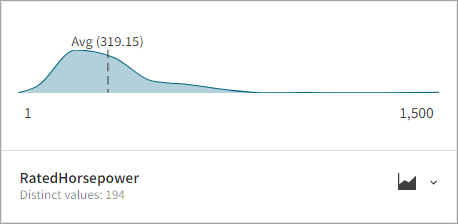
Each Binned frequency profile card provides:
- Field name
- Cardinality (distinct values)
- Histogram showing the numeric data distribution
- Minimum value
- Average value (the sum of the numbers divided by the total number of values in the dataset)
- Maximum value
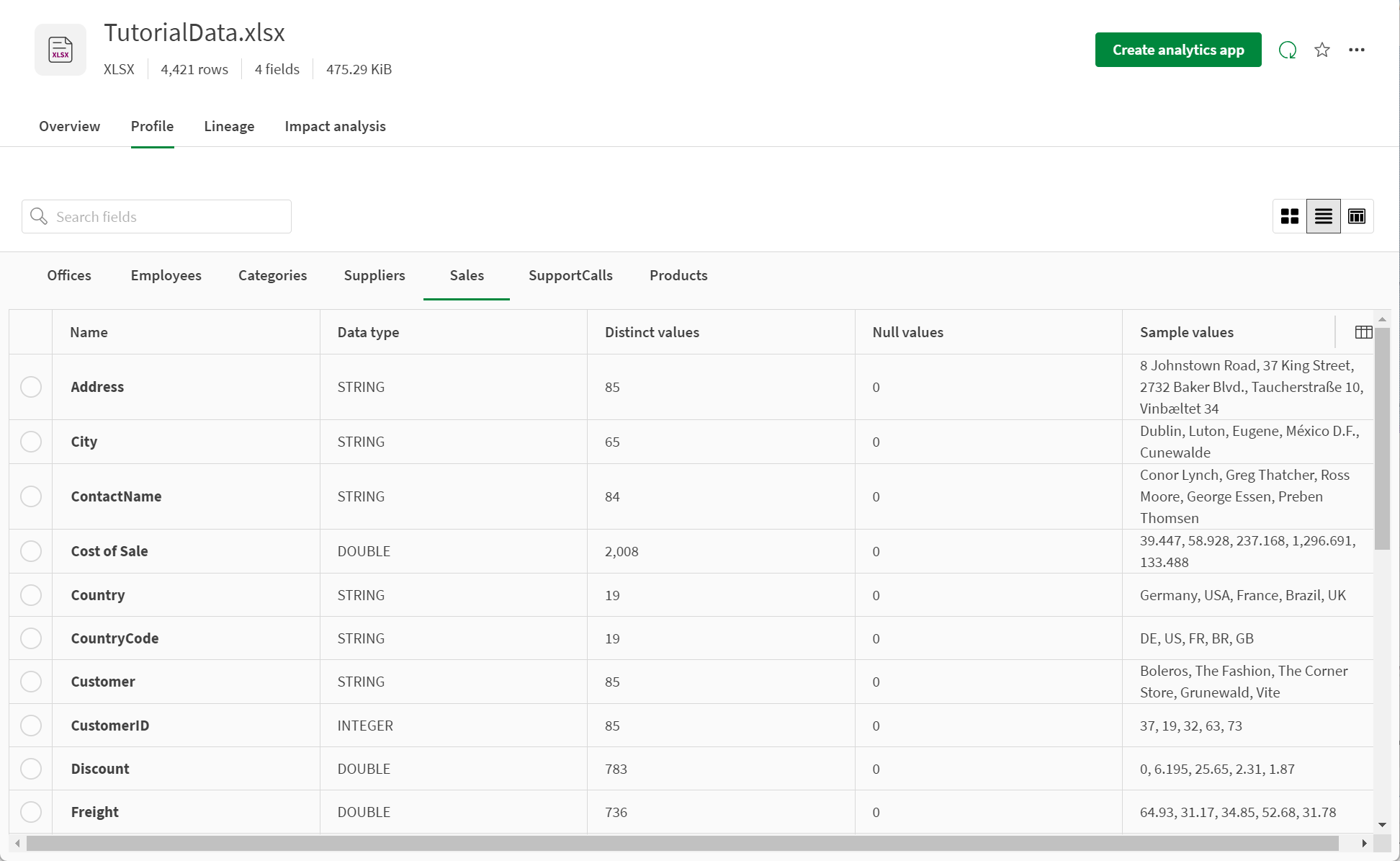
List view
Profile list view provides a table with profile statistic options. Users check the metrics of interest that are most meaningful for the dataset under the column picker , which can be found by scrolling to the far-right edge of the table. The first nine statistics are preselected by default.
List view: Select profile statistics of interest from the column picker found by scrolling right on the table
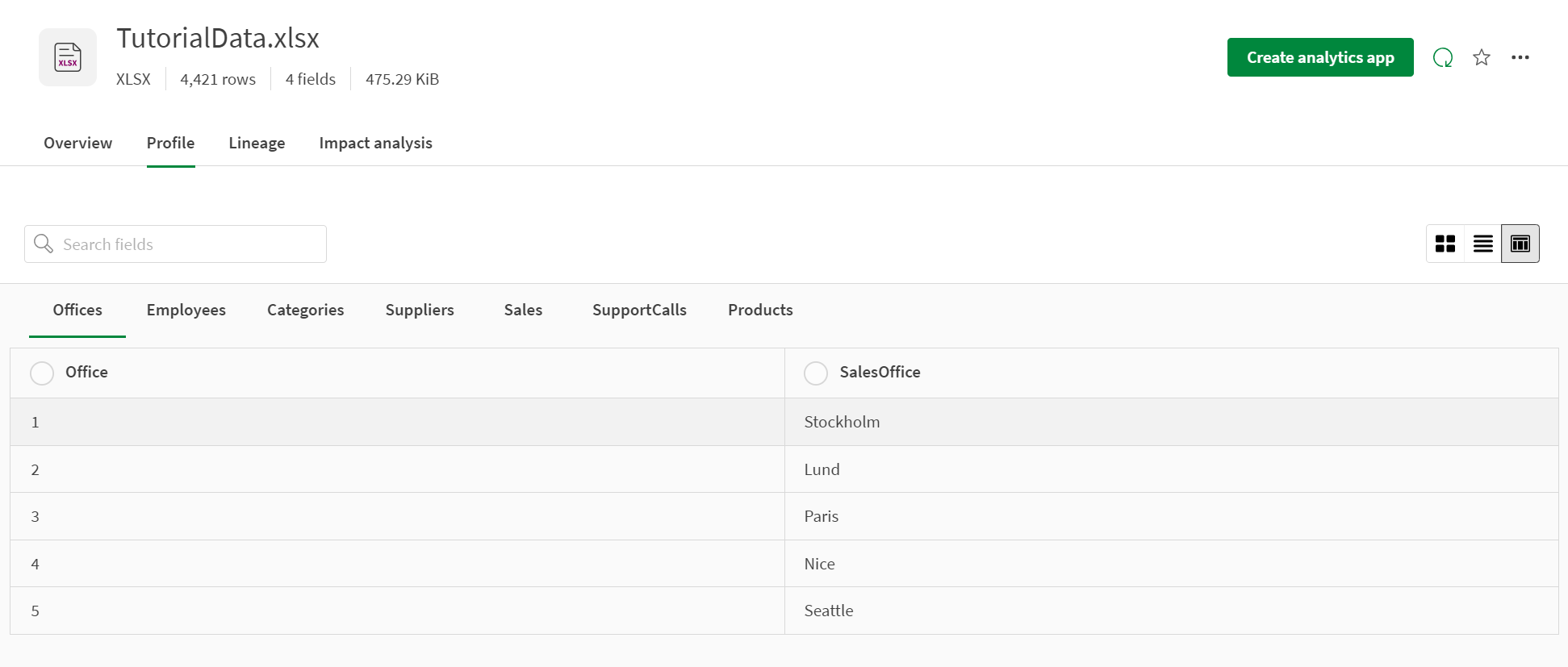
Data view
The profile data view displays your dataset as a straight data table with field column names and (up to) the first twenty values.
Data view: Dataset column names and the first twenty records display
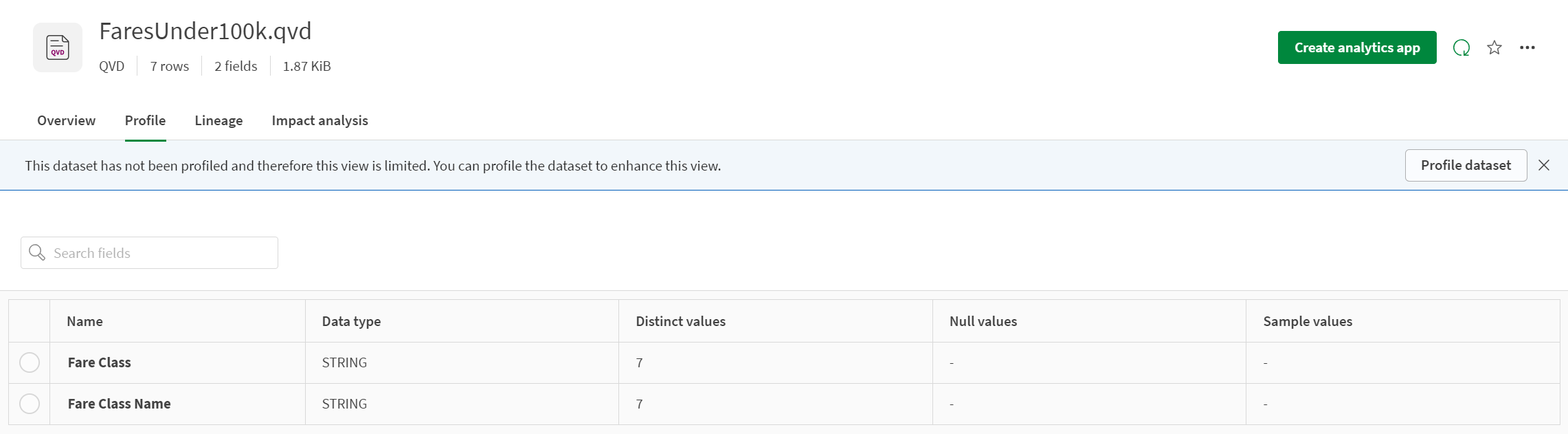
Limited profile view
Some datasets are not profiled by default. Instead, Profile displays a limited profile of the data. You can profile the data by clicking Profile dataset.
The following data types display a limited profile view until profiled:
-
QVD
-
Parquet
A limited profile of a QVD dataset