Transforming data
You can create reusable and rule-based data transformations as a part of your data pipeline. You can perform transformations as part of your data onboarding, or create reusable transformation data tasks. You can perform row-level transformations, include SQL transformations, and design complex transformation flows. The resulting datasets can either be materialized as tables, or created as views that perform transformations on the fly.
-
You can perform explicit dataset transformations, or create global rules that transform multiple datasets. You can also filter a dataset to create a subset of rows.
-
You can add SQL transformations. A SQL transformation allows you to input a SQL SELECT query into a pipeline to define complex or simple transformations.
-
You can add visual transformation flows with sources, processors and targets to define complex or simple transformations.
A transformation data task contains three views:
-
Transform
This view displays all transformations to visualize the flow from source dataset to target dataset.
-
Datasets
This view displays all basic transformations on the datasets such as filtering data, or adding columns, as well as rules to perform global transformations.
-
Model
This view lets you create a data model with the relationships between the included datasets. For more information, see Creating a data model.
In addition to storing tables in the data warehouse, you can also store tables as Iceberg tables that are managed by the data platform. This option is currently only available with Snowflake projects. This is possible by selecting Snowflake-managed Iceberg tables under Table type in the task settings.
Creating a transformation data task
The easiest way to create a transformation data task is to click ... on a storage data task and then selecting Transform data.
You can also click Create in a project and select Transform data. In this case you need to define which source data task to use.
-
Define your source data and targets in Transform.
You can either:
-
Perform dataset transformations
Select source datasets and click Add to target to add them to Target.
You can then perform basic transformations on the datasets such as filtering data, or adding columns, in Datasets.
For more information, see Managing datasets.
-
Add a SQL transformation
Select source datasets and click Add SQL transformation.
A SQL transformation allows you to input a SQL SELECT query into a pipeline to define complex or simple transformations.
For more information, see Adding SQL transformations.
-
Add a transformation flow
Select source datasets and click Add transformation flow.
The flow designer allows you to create a transformation flow with sources, processors and targets to define complex or simple transformations.
For more information, see Adding transformation flows.
-
-
You can also add more datasets from other storage data tasks by clicking Select source data.
You can add datasets from the current project, or from another project. To add datasets from another project:
-
You must have at least Can consume role in the space of the consumed project.
-
Both projects must be on the same data platform.
For more information about cross-project pipelines, see Building cross-project pipelines .
-
-
When you have added the transformations that you want, validate the datasets by clicking Validate datasets. If the validation finds errors, fix the errors before proceeding.
For more information, see Validating and adjusting the datasets.
-
Create a data model
Click Model to set the relationships between the included datasets.
For more information, see Creating a data model.
-
Click Prepare to prepare the data task and all required artifacts. This can take a little while.
You can follow the progress under Preparation progress in the lower part of the screen.
Information noteBefore you prepare a task, stop all tasks that are directly downstream. -
When the status displays Prepared, you can run the data task .
Click ... and then Run.
The data task will now start creating datasets to transform the data.
Using the Transform view
In Transform, all transformations are displayed to visualize the flow from source dataset to target dataset.
-
Select a transformation to see which source datasets are used, and which target datasets are created.
-
Select a source to see all transformations where it is used, and all resulting targets.
-
Select a target to see which are the source datasets, and which transformation created this target dataset.
Transform view in a transformation
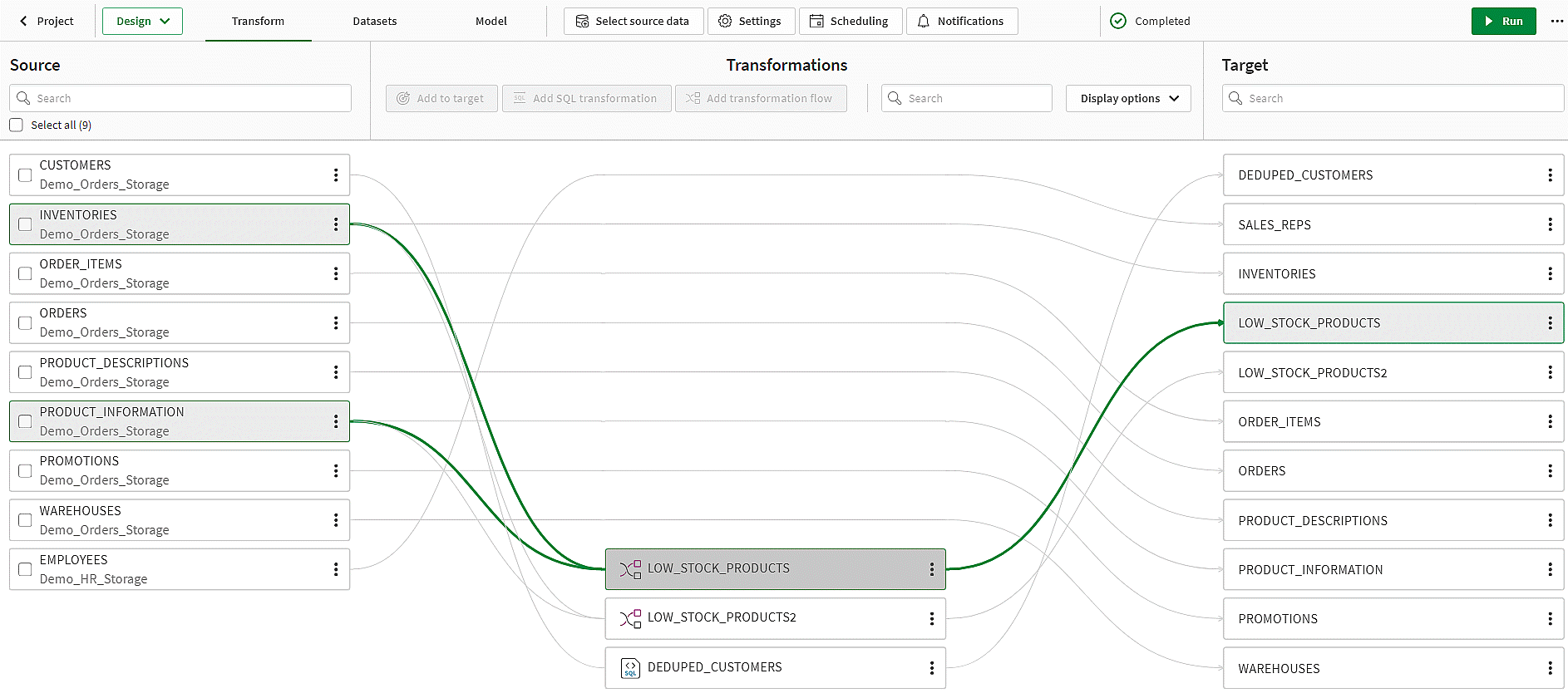
You can change the following settings by clicking Display options:
-
Filter by transformation type
Display only transformations of one or two transformation types.
-
Filter
Display all transformations or just the selected transformation. You must select a transformation to enable this option.
-
Density
Select if you want to display transformations with a compact layout, or a wide layout using more space.
Using the Datasets view
In Datasets you can view and edit all target datasets in the transformation task.
See also Managing datasets for more information.
Adding a target dataset
You can add more target datasets to the transformation task.
-
Click
.
-
Provide Name and optionally Description for the dataset.
-
Select a source dataset from the datasets available in the task in Source dataset.
Tip noteYou can select No source dataset to create a empty dataset, not connected to any source. You can add columns to the dataset during design, but you must connect to a source dataset before you can prepare the task.
The target dataset is now added.
Changing the source dataset
You can change the source dataset of a target dataset.
-
Click
after Source: [name of source dataset].
-
Select another source dataset from the datasets available in the task in Source dataset.
Tip noteYou can select No source dataset to disconnect the target dataset from the source. You can edit the dataset during design, but you must connect to a source dataset before you can prepare the task.
Adding new columns
You can add new columns to the target dataset.
-
Adding a new column from scratch
Click + Add.
Provide a name for the column, and set an expression to define the column data.
For more information, see Adding columns to a dataset.
-
Adding a column from source
Click
next to Add and select Add column from source.
Select a column from the source dataset.
Reordering columns
You can change the ordinal position of a column.
-
Select a column.
-
Click
and then Reorder.
-
Use the arrows to move the column up or down.
-
Close Change ordinal when you are ready.
Creating transformation rules
You can create re-usable transformation rules to perform global transformation on datasets.
For more information about creating rules, see Creating rules to transform datasets.
Filtering a dataset
You can filter data to create a subset of rows, if required.
-
Click
and then Filter.
For more information about filtering, see Filtering a dataset.
Scheduling a transformation task
You can schedule a transformation task to be updated periodically. You can set a time based schedule, or set the task to run when input data tasks have completed running.
Click ... on a data task and select Scheduling to create a schedule. The default scheduling setting is inherited from the settings in the project. For more information about default settings, see Transform default values.
You always need to set Scheduling to On to enable the schedule.
Time based schedules
You can use a time based schedule to run the task regardless of when the different input sources are updated.
-
Select At specific time in Run the data task.
You can set an hourly, daily, weekly or monthly schedule.
Event based schedules
You can use an event based schedule to run the task when input data tasks have completed running.
-
Select On specific event in Run the data task.
You can select if you want to run the task when any of the input tasks have completed successfully, or when any of a selection of input tasks have completed successfully.
Monitoring a transformation task
You can monitor the status and progress of a transformation task by clicking on Monitor.
For more information, see Monitoring an individual data task.
Reloading data
You can perform a manual reload of tables if the data is materialized as physical tables. This is useful when there are issues with one or more tables.
-
Open the data task and select the Monitor tab.
-
Select the tables that you want to reload.
-
Click Reload tables.
The reload will happen the next time the task is run. The reload process behaves differently depending on the history setting and transformation type of each dataset. This means that the reload process can differ between datasets in a data task.
-
Dataset transformations are reloaded by truncating and loading.
-
SQL transformations and transformation flows can be reloaded by truncating and loading, or by comparing and applying. It is best practice to compare and apply.
Reloading a dataset based on SQL transformation or transformation flow
You can cancel the reload for tables that are pending reload by clicking Cancel reload. This will not affect tables that are already reloaded, and reloads that are currently running will be completed.
Downstream tasks will be reloaded to apply changes, and to avoid backdating.
Downstream impact after reloading a Transform data task
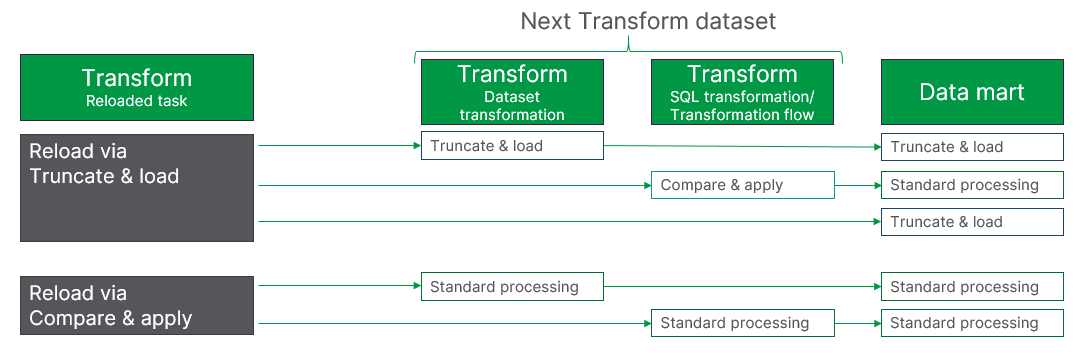
The impact downstream depends on the type of reload operation executed, and the type of immediate downstream dataset. Standard processing means that the dataset will react and process data using the configured method for the specific dataset.
Example: Reloading a dataset via truncate and load
-
If the next dataset uses dataset transformations, it will be reloaded on next execution via a truncate and load.
-
If the next dataset is a SQL transformation or transformation flow, it will be reloaded using compare and apply.
Reloading a dataset with no history
In this case, there is no history to consider. To reduce processing on the target, the reload is performed by:
-
Truncating the tables.
-
Loading current data from the upstream data task.
Downstream tasks will be reloaded to apply changes.
Reloading a dataset with history enabled
The reload is performed by:
-
Truncating current, prior, and changes tables.
-
Loading data from the upstream data task, including prior tables.
Reloading a dataset based on SQL transformation or transformation flow
-
Truncate and reload
Information noteThis option may cause loss of history.-
Truncating the current and change tables.
-
Running the query and loading it to the current tables.
-
-
Reload and compare
-
Running the query and comparing it with the current tables.
-
Adding changes.
-
Transformation settings
You can set properties for the transformation data task .
-
Click Settings.
General settings
-
Database
Database to use in the data source.
-
Task schema
You can change the name of the data task schema. Default name is the name of the task.
-
Internal schema
You can change the name of the internal storage schema. Default name is the name of the task appended with "__internal".
-
Default capitalization of schema name
You can set the default capitalization for all schema names. If your database is configured to force capitalization, this option will not have effect.
- Prefix for all tables and views
You can set a prefix for all tables and views created with this task.
Information noteYou must use a unique prefix when you want to use a database schema in several data tasks. -
Materialized
You can select to only create views that perform transformations on the fly (Non-materialized), or create both tables and views(Materialized).
-
Historical Data Store (Type 2)
You can keep historical change data to let you easily recreate data as it looked at a specific point in time. You can use history views and live history views to see historical data.
-
Publish to catalog
Select this option to publish this version of the data to Catalog as a dataset. The Catalog content will be updated the next time you prepare this task.
For more information about Catalog, see Understanding your data with catalog tools.
Runtime settings
-
Parallel execution
You can set the maximum number of connections for full loads to a number from 1 to 5.
-
Warehouse
The name of the cloud data warehouse.
View type settings
The View type settings are only applicable for Snowflake.
-
Standard views
Use Standard views for most cases.
-
Snowflake secure views
Use Snowflake secure views for views designated for data privacy or sensitive information protection, such as views created to limit access to sensitive data that should not be exposed to all users of the underlying tables.
Information note Snowflake secure views can execute more slowly than Standard views.
Table type settings
These settings are only available in projects with Snowflake as data platform.
-
Table type
You can select which table type to use:
-
Snowflake tables
-
Snowflake-managed Iceberg tables
You must set the default name of the external volume in Snowflake external volume.
-
-
Cloud storage folder to use
Select which folder to use when landing data to the staging area.
-
Default folder
This creates a folder with the default name: <project name>/<data task name>.
-
Root folder
Store data in the root folder of the storage.
-
Folder
Specify a folder name to use.
-
-
Sync with Snowflake Open Catalog
Enable this to let Snowflake Open Catalog manage the files in cloud file storage.
Best practices
-
It is not possible to change source for a dataset in a data mart if facts and dimensions have been added. If you want to be flexible, you can add a preceding Transform task with non materialized views that can be used to change sources and also to have a model for all source tasks.
Limitations
-
It is not possible to change data types in a transformation data task when the Non-materialized option is selected.
-
Field level lineage is not available for datasets created in SQL transformations or transformation flows.
