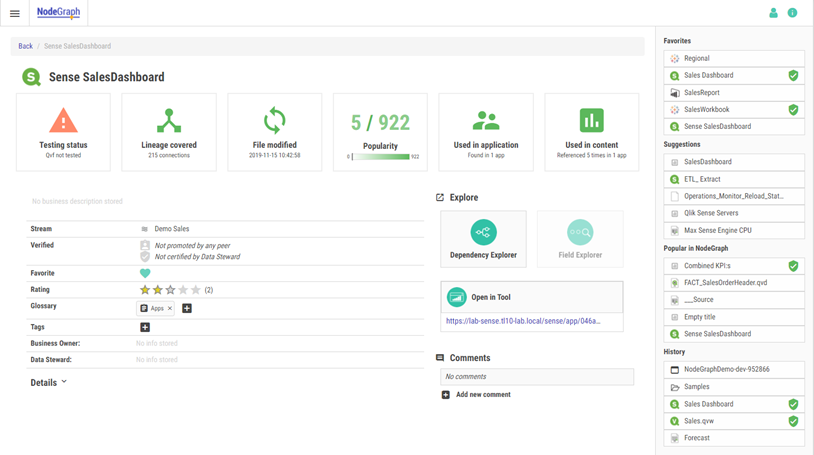
Data Catalog
The Data Catalog allows you to search and explore your data landscape.
In the settings page you can clear the catalog of all data and then sync the catalog so that all the information is included (such as QVDs, expressions, dashboards, datasets, etc.). You can also sync the Data Catalog by running the “Sync container in Data Catalog” job under the Scheduler section. Keep in mind that this will only sync the Data Catalog for the specified container.
No specific setup is required other than user roles. See Role management for more information.
NodeGraph as a single point of entry
NodeGraph knows where all apps, dashboards, KPIs etc. are in the actual BI tools. To make the navigation easy for all users, the catalog includes direct links to Qlik Sense, Tableau, and PowerBI. These links are present in shortcuts, search results, and node pages.
Links to BI Tools from Data Catalog

Data Steward functionality
In NodeGraph 4.5.0, a set of Data Steward features were introduced into the catalog. No specific role setting is used for Data Stewards for now. Instead, all users that are either Admins or Container Admins have access to this. Container Admins are limited to nodes that exist in any of their assigned containers.
These features are found in the user menu in the top-right corner, which takes the user to a custom search page.
Manage Data Catalog navigation
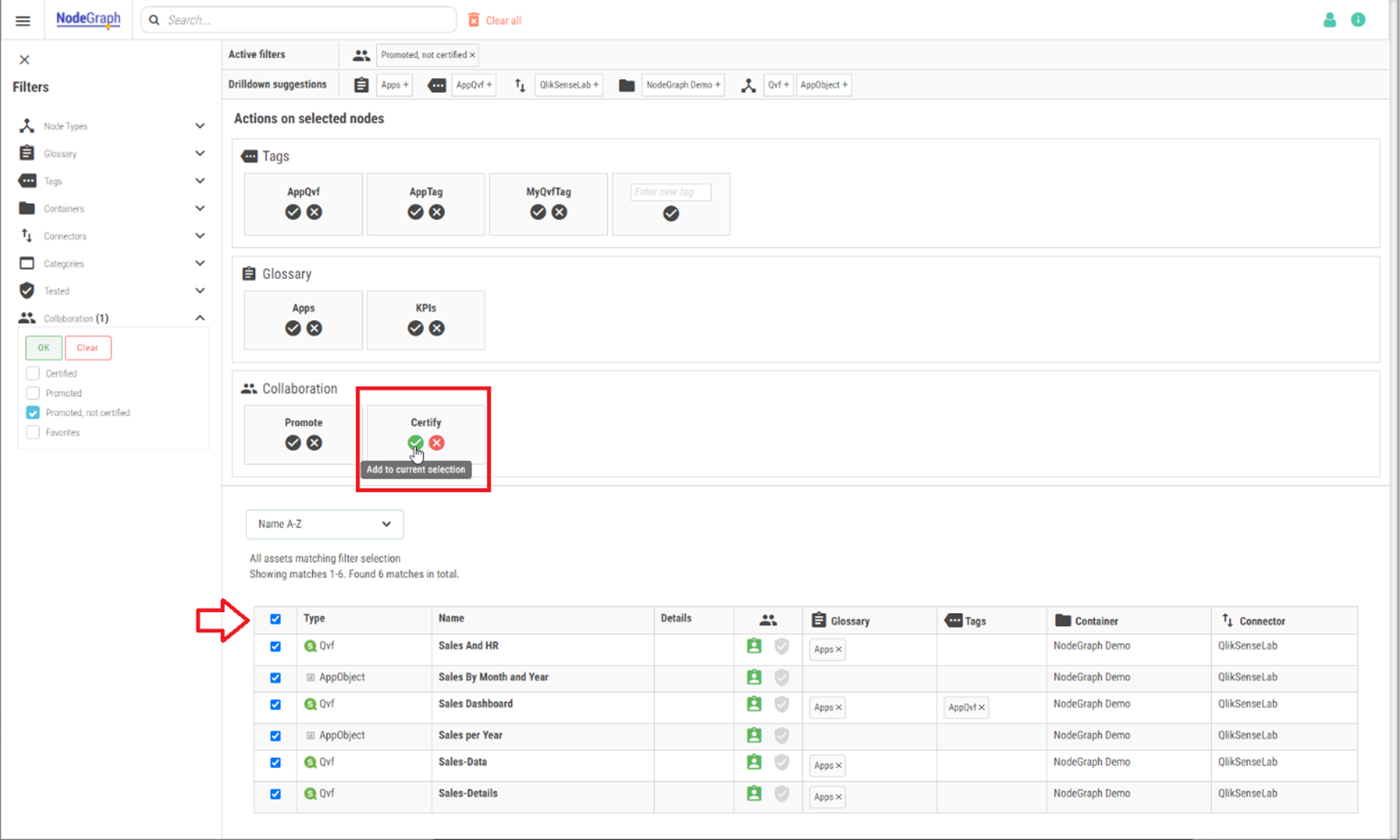
In this custom search page, the Data Steward can combine search words with filters to pinpoint specific nodes. By selecting nodes in the search result, bulk operations can be performed to add and remove tags, glossaries, and verifications. See below for more details on verifications and glossaries.
Manage Data Catalog with Data Steward features

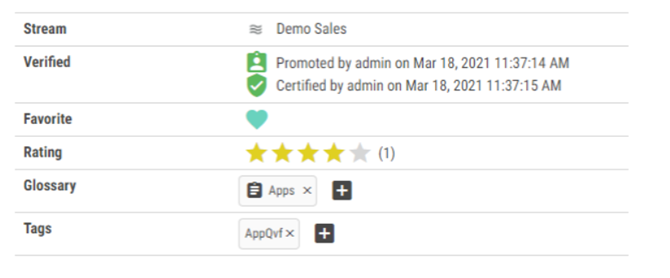
Node verification
To make it easier to find nodes of interest, a collaboration feature for node verification has been added to the Catalog. All users can promote any node that they feel could be of interest for their peers. Data Stewards can certify a node to show all users that the node fulfills any requirement that the organization might have, e.g. that a specific KPI has a valid definition, and its output has been verified.
Node promotion information
To make it easy for Data Stewards to act on nodes that have been promoted by a user, the filters can be used to show only the nodes that have been promoted, but not yet certified.
Data Steward view of uncertified nodes
Glossaries
One part of the new data steward functionality is the built-in glossaries. NodeGraph 4.5.0 comes with two default glossaries:
-
Apps
-
KPIs
Glossaries can be described as a specific tag type that data stewards can use to pinpoint nodes in the BI estate. Once glossaries are populated, the glossaries will act as a filter on the search results for basic users. This will give the data stewards the ability to hand-pick nodes to make the Catalog more specific and easier to explore.
Quick search shortcuts to the default glossaries are available on the catalog landing page.
Data Catalog landing page with glossary and quick search shortcuts
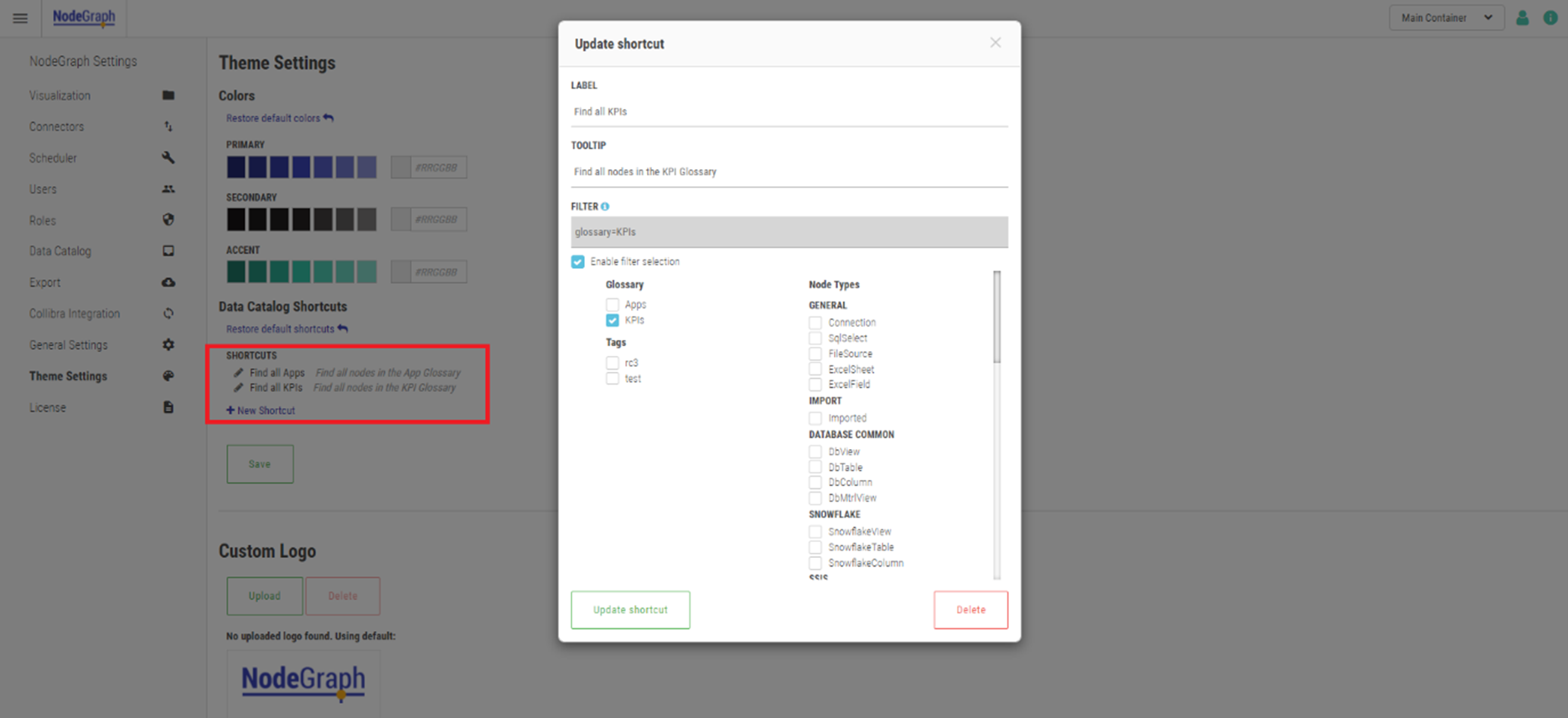
The shortcuts are managed by NodeGraph Admins in the Theming Section. Here it is possible to modify existing or create new custom shortcuts.
Update shortcut settings
Node management
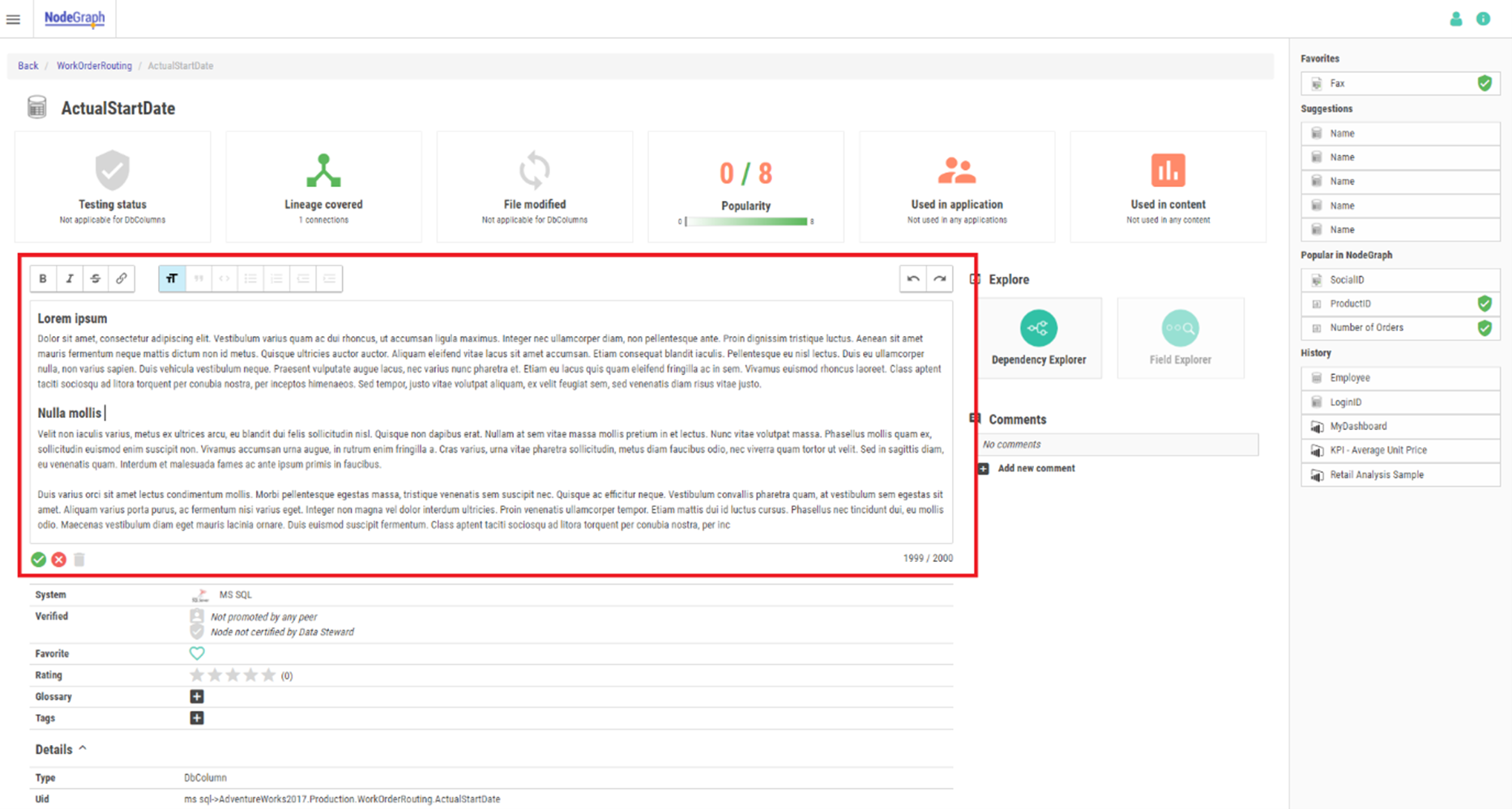
A Data Steward is also allowed to interact with a specific node by navigating to that node in the Catalog. The features found on the bulk management page are available here as well, i.e. the possibility to promote and certify the node, as well as adding tags and glossary tags to a node.
Each node also has the possibility to add a custom business description, where the Data Steward can enter edit mode to use a text editor directly on the page for editing in real time.
Data Catalog node details page with Data Steward features
Automated shortcuts
NodeGraph uses a combination of Catalog node interaction history and node content to create different types of automated node suggestions that might be of interest. The NodeGraph AI engine uses the current user and node context as input to provide different suggestions based on the current situation. The AI engine is constantly using user interactions and node content to learn over time and should be able to provide better suggestions the longer it has been in use.
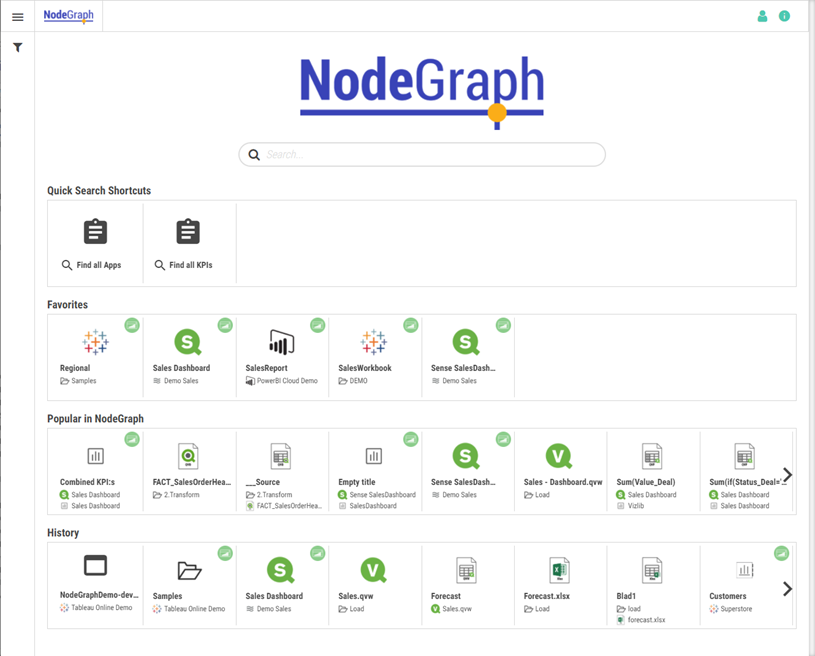
There are three different types of automated suggestions:
-
Suggestions: Based on current user and Catalog context.
-
Popular in NodeGraph: Based on other users’ interactions and Catalog context.
-
History: Based on current users’ interactions and Catalog context.
Data Catalog shortcuts on landing page
Data Catalog shortcuts on node page