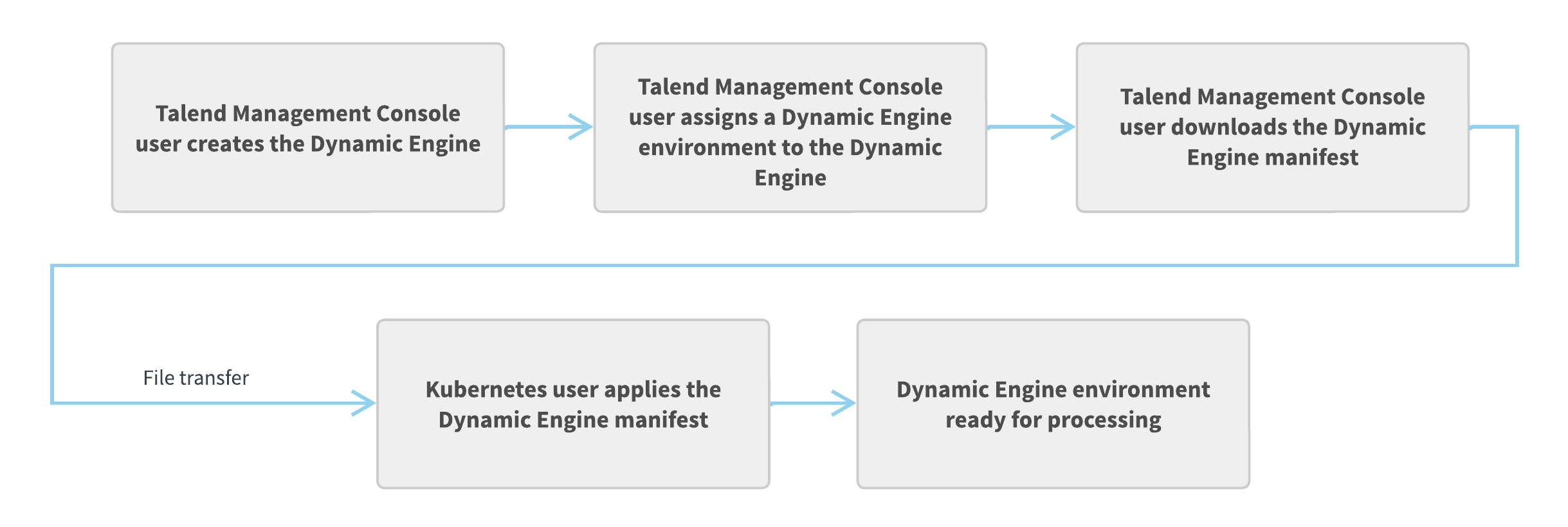
Setting up a Dynamic Engine and a Dynamic Engine environment in Kubernetes
Provide one of your own Kubernetes clusters to deploy a Dynamic Engine and its environment or environments on it.
- Create the logical entities for the engine and environments.
- Assign environments to the engine.
- Generate deployment files for the engine, environments, and their assignments.
- Apply those files to your cluster to set up the corresponding physical entities.
Adding a Dynamic Engine
Before you begin
You must have the Infrastructure Administrator (containing the TMC_CLUSTER_MANAGEMENT permission) role in Talend Management Console.
Procedure
Results
Adding a Dynamic Engine environment
Create a new environment dedicated to a Dynamic Engine.
This environment can be used with Dynamic Engines only and can be assigned to a single Dynamic Engine at a time.
Before you begin
You must have the Environment Administrator role in Talend Management Console.
Procedure
Results
The environment is created with the space you specified.
To share the space, click the environment name then click the Share space icon next to the space name from the Spaces tab.
To add other spaces to this new environment, click the environment name then Add space from the Spaces tab.
What to do next
Assigning an environment to a Dynamic Engine
Assign one or more environments to a Dynamic Engine. The next task runs from the environments will occur in the Dynamic Engine.
Assigning an environment to a Dynamic Engine overrides the existing settings of engine and run profile for that environment.
You can assign one or more environments to a Dynamic Engine from the Dynamic Engines tab directly from the list or from the drawer. You can also do it when creating a Dynamic Engine.
Before you begin
- You must have the Environment Administrator role in Talend Management Console.
- You must have the Infrastructure Administrator role (TMC_CLUSTER_MANAGEMENT) to assign Dynamic Engine environments to a Dynamic Engine.
Procedure
Results
By default, only the recommended Helm deployment file can be downloaded this way.



