Customer Service Provider
Procedure
-
Place the following components as shown in the screenshot below:
-
cBeanRegister - cMQConnectionFactory - cConfig
-
cREST - cSetBody - cWireTap
-
cSEDA - cJavaDSLProcessor - cJMS - cJavaDSLProcessor

-
-
Configure the cBeanRegister component to
customers as a Bean Id. In the
code section, we are going to populate some random data.

beans.Customers customers = new beans.Customers(); beans.Customer customer = new beans.Customer(); customer.setFirstName(TalendDataGenerator.getFirstName()); customer.setLastName(TalendDataGenerator.getLastName()); customer.setCity(TalendDataGenerator.getUsCity()); customers.addCustomer(customer); customer = new beans.Customer(); customer.setFirstName(TalendDataGenerator.getFirstName()); customer.setLastName(TalendDataGenerator.getLastName()); customer.setCity(TalendDataGenerator.getUsCity()); customers.addCustomer(customer); beanInstance = customers;You have created two Beans namely Customer and Customers.
The following is the code for the Customers Bean:
@XmlRootElement public class Customers { ArrayList<Customer> customers = new ArrayList<Customer>(); @XmlElement public ArrayList<Customer> getCustomers() { return customers; } public void setCustomers(ArrayList<Customer> customers) { this.customers = customers; } public void addCustomer(Customer customer) { if (this.customers == null) { customers = new ArrayList<Customer>(); } this.getCustomers().add(customer); } }and the following code is for the Customer Bean:
@XmlRootElement @XmlType(propOrder = { "firstName", "lastName", "city" }) public class Customer { private String firstName; private String lastName; private String city; @XmlElement(name = "firstName") public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } @XmlElement(name = "lastName") public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } @XmlElement(name = "city") public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } } -
We need to convert the data to XML format. Configure a
cConfig component to include the required jar files
and instantiate the Jaxb context.

import org.apache.camel.spi.DataFormat; import org.apache.camel.converter.jaxb.JaxbDataFormat; import javax.xml.bind.*; JAXBContext jc = JAXBContext.newInstance( beans.Customers.class); DataFormat jaxb = new JaxbDataFormat(jc); - Configure the cREST component to listen on the endpoint http://127.0.0.1:8041/services/customers. Select the option Produces JSON in Rest API Mapping.
-
Configure the cSetBody component to call the
customers Bean as shown in the screenshot
below.

- Connect the cSetBody to the cWireTap component to send an audit message to the seda component. Configure the cWireTap with URI seda:toAudit.
-
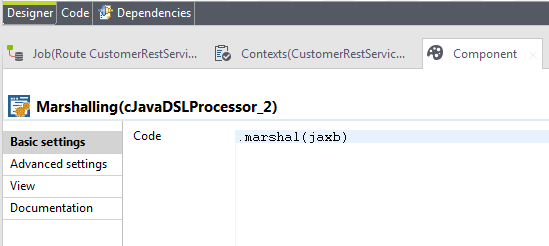
Connect the cSEDA component with the
cJavaDSLProcessor and configure it with the code
.marshal(jaxb) as shown below. Jaxb is the
DataFormat handler you already defined in the
cConfig component.
-
Connect with the cJMS and again with the
cJavaDSLProcessor with Code
.end(). Configure the Queue name
audit.

-
Run the Route and test it with a browser. You should get a customer list in
JSON format as shown below.

Now instead of deploying service to a Talend Runtime server, we will export it as a microservice.
-
In the Deployment view of the Route
tab, select Microservice in the Build
Type list. Save the Route.

-
Right click on the Route and select Build Route.

-
The Build type is set to
Microservices. Click Finish to
export the Route.

-
Locate the jar file and run it with a java command.
Java -jar CustomerProducer***.jar
Did this page help you?
If you find any issues with this page or its content – a typo, a missing step, or a technical error – please let us know!
