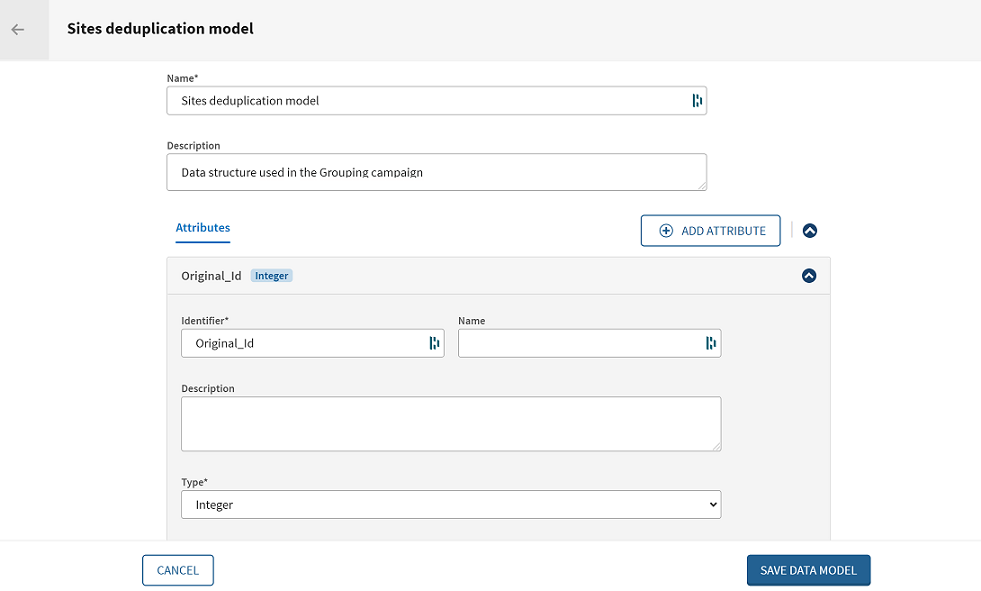
Defining a data model for the Grouping campaign
In this example, you create a data model to determine the structure of the data to be managed in the Site deduplication campaign. This campaign enables data stewards to label near duplicates in a data sample extracted by a Talend Job.
Talend Data Stewardship has data model awareness which makes possible the syntactic and semantic validation of data. You can define the attributes in the data model and select their types out of a predefined standard or semantic types.