Source connection wizard
Source connections are defined as independent top-level objects within the application and associated with sources as a prerequisite of source configuration. Analysts can apply an existing source connection to new sources or create a new source connection that can be reused. This connection object model enables flexibility; entities inherit a default source connection from a source but that connection can be switched (over-written) at the entity level. Consider the following use case: A user may want to change an entity source connection from JDBC to Sqoop so that source remains JDBC source but the data transfers via Sqoop (a faster more efficient data transport utility). Or a user may want to switch from JDBC source to FILE and reroute the data directly from HDFS.
Note that QVD sourceconnections show up in source connection lists as READ-ONLY connections; QVD source connections can only be defined and edited by administrators through QVD Import configuration in the administration module.
The wizard supports all connection types (JDBC, FILE, XML, MAINFRAME, SQOOP) and applicable Protocols (ADLS, KAFKA, FTP, SFTP, S3, HDFS, LOCALFILE, OPENCONNECTOR, WASB, WASBS). Source connections can be applied at entity level in bulk with the option to overwrite properties for individual entities.
Users will find five default source connections in a newly installed environment. From Sources grid, select Source Connections button to display the connections available for that environment.
|
Source Connection name |
Connection type |
Communication protocol |
Connection URL (example) |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
PODIUM_METADATA_CONNECTION |
JDBC |
JDBC |
jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/ md_4.0
|
Metadata repository connection. Use this connection to ingest, test and explore metadata tables. |
|
FILE_LOCALFILE_CONNECTION |
FILE |
LOCALFILE |
file:/ |
Default server connection for Flat File ingest |
|
MAINFRAME_LOCALFILE_CONNECTION |
MAINFRAME |
LOCALFILE |
file:/ |
Default server connection for Mainframe ingest |
|
XML_LOCALFILE_CONNECTION |
XML |
LOCALFILE |
file:/ |
Default server connection for XML ingest |
|
JSON_LOCALFILE_CONNECTION |
FILE |
LOCALFILE |
file:/ |
Default server conection for JSON ingest |
Default source connections

Add a new source connection
From sources screen select Source Connections
Sources grid

From source connection page, options include selecting New Source Connection button above the grid to add a new source connection, or selecting  (delete) on the connection row to delete that connection, or by selecting
(delete) on the connection row to delete that connection, or by selecting  View/Edit on the connection row to modify an existing connection.
View/Edit on the connection row to modify an existing connection.
Source Connections page

Source connection functionality can also be accessed and edited by selecting from the actions dropdown on individual entity rows (Select More then Source Connection)
Actions dropdown for individual entities

1. Adding a source connection
Users must enter the following information to initiate a new connection after selecting New Source Connection button: Connection Name, Description, Groups access is common for all connection types upon creation.
Connection Name: User defined
Description: User defined
Groups: Associate group access by selecting Group names from dropdown
Associating group access to a source connection

Connection Type: Options {FILE | JDBC | JSON | MAINFRAME | SQOOP | XML}
View connection types
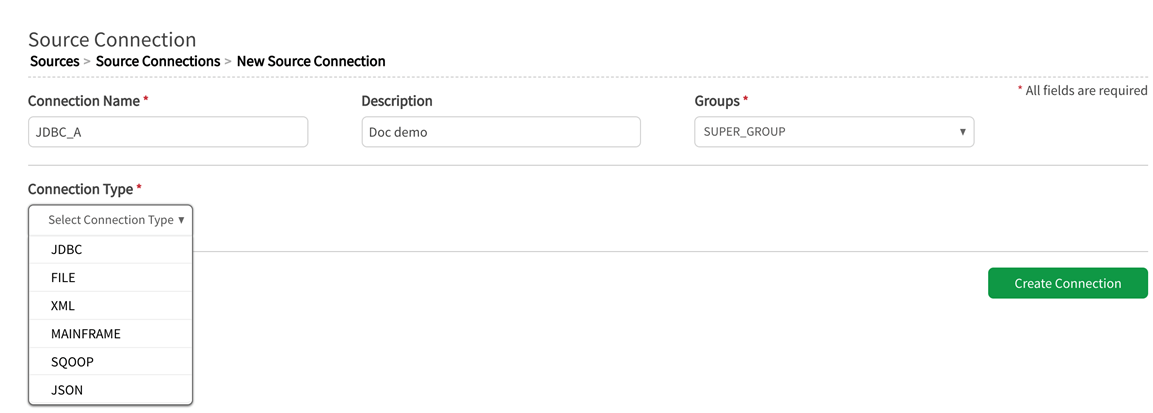
If the connection type is JDBC, JDBC Source Type dropdown will display to the right. Registered JDBC databases for the application instance populate this dropdown.
If the connection type is FILE, JSON, XML, or MAINFRAME, Protocol options dropdown will display:.ADLS, FTP, HDFS, KAFKA, LOCALFILE, OPENCONNECTOR, S3, SFTP, WASB, and WASBS.
If the Connection Type is Sqoop, no dropdown appears, because Sqoop is also a transport protocol.
JDBC Source Types
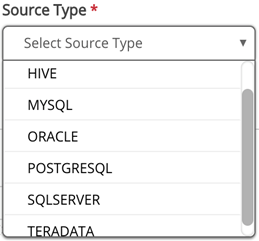
FILE, JSON, XML, MAINFRAME Protocols

2. Connection type
This selection drives which connection-specific fields are required in Connection Information. Enter the required fields and Test Connection.
Creation and View/Edit screens are identical with the exception of Create Connection | Update Connection actions in lower right of screen.
Connection type: JDBC
Once connection type is entered, a dropdown for database (MySQL, Oracle, Teradata, etc.) displays to the right and the JDBC connection information fields appear below.
Connection Information fields
Connection String:
Example:
jdbc:oracle:thin@<HOST>:<PORT>:<DATABASE_NAME>
Example:
jdbc: db2://172.24.0.20:50000/sample
User Name: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
Password: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
Select Test Connection button (Note that Sqoop does not provide a test connection feature)
Testing connection

Properties tab is to the right of Connection Information tab and provides the option to add (Add Property) additional key/value metadata upon source connection creation or update if source-specific connection properties have been defined for that connection type. Once the source connection is created, several of these properties and values will be populated.
Be sure to select Create Connection when required fields have been configured.
Source Connection properties, add property

After successful creation of source connection, additional properties and credentials populate and display: Connection Source Type, User Name, Password (encrypted), Connection String.
Additional properties and credentials

Connection Types
Connection type: File
Protocols: Options {ADLS | FTP | HDFS | KAFKA | LOCALFILE | OPENCONNECTOR | S3* | SFTP | WASB | WASBS}
Connection Information:
Connection String: file:/ or hdfs:// or s3a:// or adl:// (ADLS Gen1) or abfs[s]:// (ADLS Gen2), etc., depending on protocol
User Name: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
Password: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
*AWS S3 schema: Scheme s3 should be used when Qlik Catalog is run in EMR (where it is maintained by AWS and is up-to-date). Scheme s3a should be used otherwise. Scheme s3n is obsolete and should not be used.
OPENCONNECTOR protocol is used only to land flat files into HDFS LoadingDock for ingest.
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | FILE |
| Protocol | LOCALFILE |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String | file:/ |
| User Name | (optional) |
| Password | (optional) |
Connection Type: File, Protocol: LOCALFILE (screenshot example)

|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | FILE |
| Protocol | ADLS |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String | syntax: abfss://<container>@<storage_account_name>.dfs.core.windows.net/ example: abfss://abfstest@exadlsgen2test1.dfs.core.windows.net/ |
| User Name | <storage_account_name> |
| Password | access key |

ADLS Gen2 notes
-
Note that the <storage_account_name> value used to build the connection string is the User Name entry.
-
The storage account in MS Azure must be created with specific options. On the Advanced tab in storage account settings: In the Security section, Enable storage account key access must be checked; and in the Data Lake Storage Gen2 section, Enable hierarchical namespace must be checked.

|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | FILE |
| Protocol | FTP |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String | ftp://192.168.126.xx:xx |
| User Name | ftpuser |
| Password | xxxxxxx |
Connection Type: FILE, Protocol: FTP (screenshot example)

|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | FILE |
| Protocol | KAFKA |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String | kafka://hostname.corp.namedata.com:9092 |
| User Name | (optional) |
| Password | (optional) |
Connection Type: FILE, Protocol: Kafka (screenshot example).

Kafka notes
- Qlik Catalog uses batch processing for Kafka loads like all other load protocols. The application reads directly from Kafka during the receiving step; the loading dock step is skipped.
- Kafka cannot be used for new sources, it can only be applied for loads of source environments that are already in the application.
- Users can specify a Kafka host, topic, offset and optional partition number. These properties apply at the source connection and entity level.
- Kafka is the only load type that never consumes a file in the entire load process. Data starts on Kafka and gets loaded into memory.
- Kafka is only supported for FILE, JSON, XML Source types (not mainframe or JDBC)
- Archiving is not supported for Kafka even if enabled via enable.archiving property. Kafka is already residing on the cluster and servers as the record of original data.
Setup for Kafka ingest involves establishing the source connection, then establishing the entity and specifying the Kafka Topic Name in Add Data wizard. The URI field or connection.string (below) is required and this should be an established Kafka broker. Once the entity is created, Kafka entity-level properties (shown below) can be set or reset. Kafka properties are also detailed in SourceàSource Properties in webhelp.
Kafka source connection default properties populate upon entry of qualified Kafka URI:
- kafka.max.total.records=1000 (default value). Maximum number of records to consume from Kafka in one load.
- kafka.poll.timeout.ms=10000 (default value). Timeout for one poll of the Kafka queue. This each poll tries to consume up to 100 records. Several polls may be made per load.
- kafka.record.buffer.size=1000 (default value). Size, in records, of the buffer while pulling data from Kafka.
- kafka.start.offset=END (default value). Can be one of: END, BEGINNING, <long integer value>). Starting position for the next Kafka load.
Kafka properties in Source Connection
|
Property |
Value |
|---|---|
| conn.user.password | #0(poirxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx) |
| connection.string | kafka://hostname.corp.namedata.com:9092 |
| kafka.max.total.records | 1000 |
| kafka.poll.timeout.ms | 10000 |
| kafka.record.buffer.size | 1000 |
| kafka.start.offset | END |
Protocol: Kafka (properties screenshot example)

Connection type: XML
Protocols: Options {ADLS | FTP | HDFS | KAFKA | LOCALFILE | S3 | SFTP | WASB | WASBS}
Connection Information:
Connection String: file:/ or hdfs:// or s3a:// or adl:// (ADLS Gen1) or abfs[s]:// (ADLS Gen2), etc., depending on protocol
User Name: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
Password: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | XML |
| Protocol | HDFS |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String | hdfs://hostname-nameservice:8020/ |
| User Name | (optional) |
| Password | (optional) |
Connection Type: XML, Protocol: HDFS (screenshot example)

Connection type: JSON
Protocols: Options {ADLS | FTP | HDFS | KAFKA | LOCALFILE | S3 | SFTP | WASB | WASBS}
Connection Information:
Connection String: file:/ or hdfs:// or s3a:// or adl:// (ADLS Gen1) or abfs[s]:// (ADLS Gen2), etc., depending on protocol
User Name: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
Password: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | JSON |
| Protocol | SFTP |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String | sftp://192.168.xxx.xx |
| User Name | ftpuser |
| Password | xxxxxxxxxx |
Connection type: JSON, Protocol: FTP (screenshot example)

Connection type: MAINFRAME
Protocols: Options {ADLS | FTP | HDFS | LOCALFILE | OPENCONNECTOR | S3 | SFTP | WASB | WASBS}
Connection Information:
Connection String: For example: s3a://test.nnnvpn.com/
User Name: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
Password: Optional, user defined (can be changed upon edit of source connection)
Connection type: Mainframe, Protocol: S3 (example)
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | MAINFRAME |
| Protocol | S3 |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String | s3a://test.nnnvpn.com |
| User Name | (optional) |
| Password | (optional) |
Connection type: Mainframe, Protocol: S3 (screenshot example)

Connection type: SQOOP
(No protocol—Sqoop is the transport utility)
Connection Information:
Connection String: jdbc:<db_type>://<HOST>:PORT>;<databaseName>
User Name: Optional
Password: Optional
SQOOP Connection information (Note that Sqoop does not provide a Test Connection feature)
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | SQOOP |
| Protocol | [SQOOP] |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String | jdbc:oracle:thin@xxx.xxx.xxx.xx.xxxx:XE |
| User Name | (optional) |
| Password | (optional) |
Connection type: Sqoop, Protocol: (Sqoop) (screenshot example)

SQOOP Connection Properties:
- conn.sqoop.mappers.count: User-defined (default = '4')
- conn.sqoop.schema.name: Name of source table, manually defined by user—some databases will not require (or allow) schema name and so this value will be null for some databases.
- conn.sqoop.table.name: Users can enter <$EntityName> if the source connection applies to multiple entities. A table name can be entered if the source connection will always be applied to the same table.
- conn.user.name: Entered/populated upon creation of source connection
- conn.user.password: Entered/populated upon creation of source connection
- connection.string: Location of source table
Example values for Sqoop connection properties
|
Property |
Value |
|---|---|
| conn.sqoop.mappers.count | 4 |
| conn.sqoop.schema.name | Value |
| conn.sqoop.table.name | $EntityName |
| sqoop.enclosed-by | " |
| sqoop.null-non-string | " " |
| sqoop.null-string | " " |
Protocol: Sqoop (properties screenshot example)

Apply new ingest source connection to an entity
Users are able configure source connections so that one interrogates the environment to configure technical metadata environment and then a second Ingest Source Connection is applied to entities for data ingest. The following example details a case where a source is discovered and an entity created through browsing Hive via JDBC source connection to establish the metadata and then an ingest connection routes data directly from HDFS.
The following example illustrates this process. An entity has been created by staging through the JDBC source creation wizard after applying a source connection where Connection Type is JDBC and Source Type is Hive (Hive connection value is found in About: Settings: DISTRIBUTION: distribution.uri). This process imports the technical metadata.
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
| Connection Type | JDBC |
| Protocol | HIVE |
| Connection Information | |
| Connection String |
jdbc:hive2://hostname-cloudera.corp.domaindata.com:10000/default;principal=hive/hostname-cloudera.corp.domaindata.com@HOSTNAME.REALM |
| User Name | myname |
| Password | xxxxxx |
Connection Type: JDBC, Protocol: Hive (screenshot example)

Using this source connection, a user can browse using the JDBC wizard, search for and create an entity under that source.
BEFORE ingesting data to that new entity, apply new source connection. For this example, a new source connection is created with Source Type: File and Communication Protocol: HDFS for ingest from HDFS.
HDFS connection string is found in About: Settings: LOADING DOCK: loadingdock.uri.
This connection will access HDFS directory. (Note that entity-level src.file.glob property will have to be updated)
Select the entity in source, Select General Information, at the bottom of that modal select Use Different Source Connection for Ingest.
Apply the new Source Connection (ex.name: 'FILE_HDFS') for ingest and Save.
Therefore, entity information will show the Source Connection as JDBC_Hive and the Ingest Source Connection as FILE_HDFS.


Update and save the entity property src.file.glob filepath value, example: /temp/qdc/nemo/receiving/employees/departments_profile/20200409145757/good/good-m-00000
Data can now be loaded to the entity from specified path.
Apply new Source Connection to multiple entities
Qlik Catalog allows the application of a source connection to one or more entities. Multi-select entities and then select Source Connection button from the entities grid.
Selection of multiple entities for application of a Source Connection

Apply Source Connection modal provides dropdown of available source connections to apply to multiple entities . The modal lists which entities require property updates.

Managing Entities with new Source Connections: Properties update
When a new source connection is applied to an entity, mandatory property updates may be required. The following table summarizes the property modifications updated for each scenario.
Many of these changes occur automatically, this table provides information about those changes.
Link to the applicable source connection transition:
|
Properties affected |
Properties added |
Required action/guidelines |
|---|---|---|
|
src.file.glob |
Manually add filepath |
|
|
header.validation.pattern |
Should be blank (unless header.validation.pattern.is.regex is set to True) |
|
|
header.validation.pattern.is.regex |
False (default) |
|
|
record.open.quotes |
<blank> (default) Default is blank but depends on datafile (in src.file.glob) If datafile contains records in open/close quotes then user must specify them for this property. |
|
|
record.close.quotes |
<blank> (default) Default is blank but depends on datafile (in src.file.glob) If datafile contains records in open/close quotes then user must specify them for this property. |
|
|
default.field.embedded.enclosure.scheme |
NONE |
|
|
header.line.count |
0 (default) Tip note
If the file loads with one ugly record, it might be because the file has a header, in which case try setting this value to 1. |
|
|
record.record.terminator |
ANY_NEWLINE |
|
|
src.file.glob (OPENCONNECTOR PROTOCOL only) |
<script>( manually add) |
|
|
src.file.glob (KAFKA protocol only) |
user must manually enter topic name (delete any pre-existing value/query) |
|
|
entity.custom.script.args (OPENCONNECTOR PROTOCOL only) |
Manually add this property at the entity level. This is a required property for OPENCONNECTOR protocol when using DistCp or SCP/SSH scripts. Example: Examples: (SCP) /root/custom/podium/put_file_hdfs.sh %prop.sfile %prop.starget %loadingDockLocation |
|
|
Script Properties/Values (OPENCONNECTOR PROTOCOL only) Example: p1 Example: starget |
OPENCONNECTOR script arguments. Example: Examples: SCP: [(sfile, '/datasets/m1_receipt/*jan*'), (starget,'/staging/m_1receipt.jan')] |
