Database driver registration
Users must register drivers for all JDBC source databases. This is a two step process: (1) copying JDBC driver jar files into the appropriate directory; and (2) using the Administration module to register the driver (if not already present).
JDBC driver library jar files for your licensed RDBMS should be placed in the directory called out by the following core_env property. This directory is preferred over placing drivers in $TOMCAT_HOME/webapps/qdc/WEB-INF/lib, where they will be overwritten on upgrade and where they may interfere with other libraries.
# An alternate directory to WEB-INF/lib for JDBC driver jars.
# May also be set directly, for a given driver, on table
# podium_core.pd_jdbc_source_info, column alt_classpath.
# Restart required. Default: not set
jdbc.alternate.classpath.dir=/usr/local/qdc/jdbcDrivers
If a JDBC driver is particularly complicated and consists of multiple jars (e.g., the Simba Google BigQuery driver has dozens of jars), it can be further isolated into its own sub-directory. If you do this, you must run an SQL statement as follows (default password is “nvs2014!”; update path and name):
psql podium_md -U podium_md -c "update podium_core.pd_jdbc_source_info set alt_classpath = '/usr/local/qdc/jdbcDrivers/simbaBigQuery' where sname = 'BIGQUERY';"Administration (top navigation bar) provides a wizard for the modular registration of databases; the database name populates as an option when registering sources to Qlik Catalog via JDBC. To initiate the driver registration wizard from the Administration screen, select Database Drivers from the menu ribbon at the top of the screen then select Add Driver.
Database Driver registration

The Driver Registration wizard offers the following fields:
- Name (required): Database name, user-defined (examples: Oracle, DB2, Teradata, SQL Server).
- Driver Class Name (required): Used to load the appropriate JDBC driver (example: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver).
-
Escape Character (Start): {ENUM VALUES: " ' ", (single quote) | " " ", (double quote) | " [ ", (opening bracket)}.
Information noteStart/Stop Escape Characters are not required unless column/table names contain reserved words, leading/trailing spaces, or special characters/embedded spaces.
- Escape Character (Stop): {ENUM VALUES: " ' ", (single quote) | " " ", (double quote) | " ] ", (closing bracket)}.
- Connection String Pattern (required): Syntax for JDBC URLs (example: jdbc:mysql://<HOST>:<PORT>/<DB>).
|
Name |
Driver Class Name |
ESC CHAR (open) |
ESC CHAR (close) |
Connection String Pattern |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLICKHOUSE | ru.yandex.clickhouse.ClickHouseDriver |
` (Backtick key) |
` (Backtick key) |
jdbc:clickhouse://<HOST>:<PORT>/<DATABASE> Note: Driver available at the following link:
https://github.com/ClickHouse/clickhouse-jdbc/releases/download/v0.2.6/clickhouse-jdbc-0.2.6-shaded.jar |
| DATABRICKS | com.simba.spark.jdbc41.Driver | " | " |
jdbc:spark://<HOST>:<PORT>/<SCHEMA> Note: https://databricks.com/spark/odbc-driver-download Get the 41 jar (not 4); Get SparkJDBC41.jar |
|
DB2 |
com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver |
" |
" |
jdbc:db2://<HOST>:<PORT>/<DB> |
|
HIVE |
org.apache.hive.jdbc.HiveDriver |
` |
` |
jdbc:hive2://<HOST>:<PORT>/<DATABASE_NAME> |
|
INFORMIX |
com.informix.jdbc.IfxDriver |
" |
" |
jdbc:informix-sqli://<HOST>:<PORT>/<DB>:INFORMIXSERVER=<SERVER_NAME> Note: INFORMIX database settings require that if the double-quote is used as open/close escape character, the connection string must be modified (append: ";DELIMIDENT=Y") |
|
MYSQL |
com.mysql.jdbc.Driver |
` |
` |
jdbc:mysql://<HOST>:<PORT>/<DB> |
|
ORACLE |
oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver |
" |
" |
jdbc:oracle:thin@<HOST>:<PORT>:<DB> |
|
POSTGRES |
org.postgresql.ds.PGSimpleDataSource |
" |
" |
jdbc:postgresql://<HOST>:<PORT>/<DB> |
| SNOWFLAKE | net.snowflake.clientjdbc.SnowflakeDriver | " | " | jdbc:snowflake://<account_name>snowflakecomputing.com/<connection_params>; |
|
SQLSERVER |
com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
|
[ |
] |
jdbc:sqlserver://<HOST>:<PORT>;databaseName=<DATABASE_NAME> Note: -The default driver for SQL Server on Linux does not support Windows Auth and the JTDS driver is needed http://jtds.sourceforge.net/ -Examples of connection strings with JTDS: jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://name_sql:1433/NAMEPQ;useNTLMv2=true;instance=nameqlwbs12; jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://name_sql:1433;databaseName=NAME;useNTLMv2=true;instance=nameqlwbs12; jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://RANDOQLD02.name.company.net:1433;databaseName=WideWorldName;useNTLMv2=true;instance=DSC2D;domain=NAMEDOMAIN1 |
|
SYBASE |
com.sybase.jdbc2.jdbc.SybDriver |
" |
" |
jdbc:sybase:Tds:<HOST>:<PORT> |
|
TERADATA |
com.teradata.jdbc.TeraDriver |
" |
" |
jdbc:teradata://<HOST>/dbs_port=<PORT>,database=<DATABASE_NAME> |
Sample Database Driver Registration

Optional Parameters
Excluded Schemas
List tables/schemas to be excluded (if for example, a table is a sample table or due to security issues, a schema should be bypassed).
Excluded Schemas

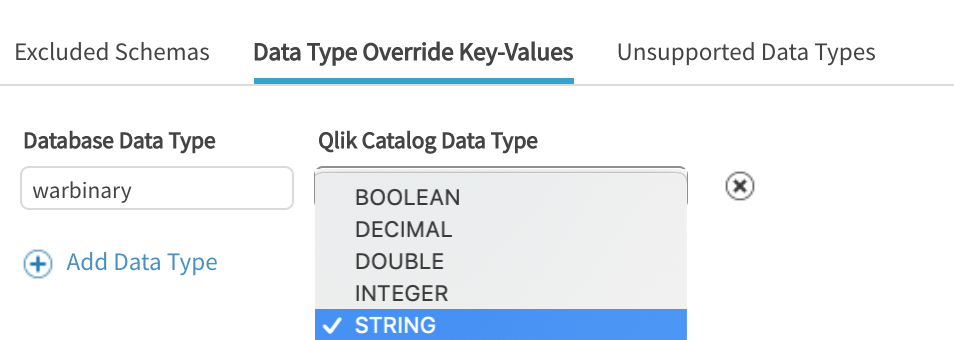
Data Type Override Key-Values
Users can over-ride datatype to a different supported type (example:" integer:STRING" for a use case where users would like to add leading zeros to field). Refer to the next subsection, Database Mappings, for External to Internal Mappings for databases and datatypes relevant to those databases. Note that users are not limited to the databases listed; common datatype mappings will be consistent across databases.
Data Type Override Key-Values
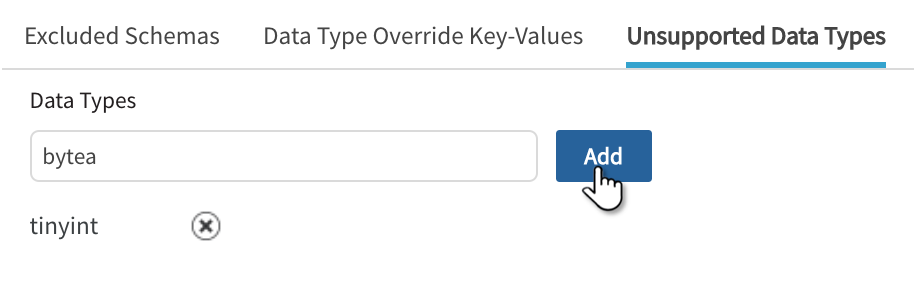
Unsupported Data Types
Qlik Catalog JDBC filters out unsupported data types while ingesting remaining supported columns. This field will vary with type of database registered. When Qlik Catalog encounters an unsupported data type, if the type cannot be converted to string it is skipped (an INFO message appears in application logs indicating the unsupported column was skipped). Entities that consist of unsupported data types are skipped with an INFO message indicating why the entity was skipped.
Database Mappings
The content below displays conversions between external and internal representations of data when data is ingested from external sources into Qlik Catalog. It is noted when external DECIMAL datatypes are mapped to internal DECIMAL datatypes (if DECIMAL is enabled via property use.decimal.instead.of.double=true). Unsupported data types are greyed out (where external types map to 'null', ex.'bytea(9)=>null'). Datatypes with different parameters map to different internal types for that database (ex. for PostgreSQL: bit(1)=>BOOLEAN and bit(32)=>INTEGER).
Users are not limited to the databases listed; common datatype mappings will be consistent across databases.
Links to databases:
Database mappings by database
Standard datatype mapping/conversions
VarChar(9) Character Set Graphic=>STRING
bit varying(1)=>BOOLEAN
INTEGER=>INTEGER
DOUBLE=>DOUBLE
DECIMAL=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
STRING=>STRING
DATE=>STRING
TIMESTAMP=>STRING
BOOLEAN=>BOOLEAN
ANSI-SQL
CHARACTER=>STRING
CHAR=>STRING
CHARACTER VARYING=>STRING
VARCHAR=>STRING
NATIONAL CHARACTER=>STRING
NCHAR=>STRING
NATIONAL CHARACTER VARYING=>STRING
NVARCHAR=>STRING
CHARACTER(9)=>STRING
CHAR(9)=>STRING
CHARACTER VARYING(9)=>STRING
VARCHAR(9)=>STRING
NATIONAL CHARACTER(9)=>STRING
NCHAR(9)=>STRING
NATIONAL CHARACTER VARYING(9)=>STRING
NVARCHAR(9)=>STRING
BIT=>BOOLEAN
BIT(1)=>BOOLEAN
BIT(32)=>INTEGER
BIT VARYING=>BOOLEAN
BIT VARYING(1)=>BOOLEAN
BIT VARYING(32)=>INTEGER
INTEGER=>INTEGER
SMALLINT=>INTEGER
BIGINT=>INTEGER
FLOAT=>DOUBLE
REAL=>DOUBLE
DOUBLE PRECISION=>DOUBLE
DATE=>STRING
TIME=>STRING
TIME WITH TIME ZONE=>STRING
TIMETZ=>STRING
TIMESTAMP=>STRING
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE=>STRING
TIMESTAMPTZ=>STRING
DB2
CHARACTER(9)=>STRING
VARCHAR(9)=>STRING
CLOB(9)=>STRING
GRAPHIC(9)=>STRING
VARGRAPHIC(9)=>STRING
DBCLOB(9)=>STRING
BINARY(9)=>null
VARBINARY(9)=>null
BLOB(9)=>null
SMALLINT=>INTEGER
INTEGER=>INTEGER
INT=>INTEGER
BIGINT=>INTEGER
DECFLOAT=>DOUBLE
REAL=>DOUBLE
DOUBLE=>DOUBLE
DATE=>STRING
TIME=>STRING
TIMESTAMP=>STRING
XML=>STRING
CHAR(9) FOR BIT DATA=>null
CHARACTER(9) FOR BIT DATA=>null
VARCHAR(9) FOR BIT DATA=>null
VARCHAR2(9) FOR BIT DATA=>null
Hive
TINYINT=>INTEGER
SMALLINT=>INTEGER
INT=>INTEGER
BIGINT=>INTEGER
FLOAT=>DOUBLE
DOUBLE=>DOUBLE
DECIMAL=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
TIMESTAMP=>STRING
DATE=>STRING
STRING=>STRING
VARCHAR=>STRING
CHAR=>STRING
BOOLEAN=>BOOLEAN
Impala
BIGINT=>INTEGER
BOOLEAN=>BOOLEAN
CHAR=>STRING
DECIMAL=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
DECIMAL(9)=>INTEGER
DECIMAL(9,0)=>INTEGER
DECIMAL(9,2)=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
DOUBLE=>DOUBLE
FLOAT=>DOUBLE
INT=>INTEGER
REAL=>DOUBLE
SMALLINT=>INTEGER
STRING=>STRING
TIMESTAMP=>STRING
TINYINT=>INTEGER
VARCHAR=>STRING
Informix
BIGINT=>INTEGER
BIGSERIAL=>INTEGER
BSON=>STRING
CHAR(9)=>STRING
CHARACTER(9)=>STRING
CHARACTER VARYING (9)=>STRING
CHARACTER VARYING (9,8)=>STRING
DATE=>STRING
DATETIME=>STRING
DEC(9)=>INTEGER
DEC(9,0)=>INTEGER
DEC(9,2)=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
DECIMAL(9)=>INTEGER
DECIMAL(9,0)=>INTEGER
DECIMAL(9,2)=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
DOUBLE PRECISION=>DOUBLE
FLOAT=>DOUBLE
FLOAT(10)=>DOUBLE
INT=>INTEGER
INT8=>INTEGER
INTEGER=>INTEGER
INTERVAL=>null
MONEY(13,2)=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
NCHAR(9)=>STRING
NVARCHAR(9)=>STRING
REAL=>DOUBLE
SERIAL=>INTEGER
SERIAL8=>INTEGER
SMALLFLOAT=>DOUBLE
SMALLINT=>INTEGER
TEXT=>STRING
VARCHAR(9)=>STRING
VARCHAR(9,8)=>STRING
BLOB=>null
binary18=>null
binaryvar=>null
BOOLEAN=>BOOLEAN
CLOB=>STRING
LVARCHAR(9)=>STRING
MySQL
BIT=>BOOLEAN
BIT(1)=>BOOLEAN
BIT(2)=>INTEGER
BIT(63)=>INTEGER
BIT(64)=>INTEGER
BIT(65)=>null
TINYINT=>INTEGER
TINYINT UNSIGNED=>INTEGER
BOOL=>BOOLEAN
BOOLEAN=>BOOLEAN
SMALLINT=>INTEGER
SMALLINT UNSIGNED=>INTEGER
MEDIUMINT=>INTEGER
MEDIUMINT UNSIGNED=>INTEGER
INTEGER=>INTEGER
INTEGER UNSIGNED=>INTEGER
INT=>INTEGER
INT UNSIGNED=>INTEGER
BIGINT=>INTEGER
BIGINT UNSIGNED=>INTEGER
DECIMAL=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
DEC=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
FIXED=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
NUMERIC=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
DECIMAL UNSIGNED=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
DEC UNSIGNED=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
FIXED UNSIGNED=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
NUMERIC UNSIGNED=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
FLOAT=>DOUBLE
DOUBLE=>DOUBLE
DOUBLE PRECISION=>DOUBLE
DATE=>STRING
DATETIME=>STRING
TIMESTAMP=>STRING
TIME=>STRING
YEAR=>INTEGER
CHAR(9)=>STRING
NATIONAL CHAR(9)=>STRING
VARCHAR(9)=>STRING
NATIONAL VARCHAR(9)=>STRING
BINARY(9)=>null
VARBINARY(9)=>null
TINYBLOB(9)=>null
TINYTEXT(9)=>STRING
BLOB(9)=>null
TEXT(9)=>STRING
MEDIUMBLOB(9)=>null
MEDIUMTEXT(9)=>STRING
LONGBLOB(9)=>null
LONGTEXT(9)=>STRING
ENUM('x-small', 'small', 'medium', 'large', 'x-large')=>STRING
Oracle
Oracle's JDBC connector documentation states that the Oracle datatype FLOAT will be listed in JDBC as NUMBER. Qlik Catalog only sees then what is exposed in JDBC. Datatypes that present in client environments as FLOAT appear in Qlik Catalog as NUMBER.
CHAR=>STRING
CHAR(9)=>STRING
VARCHAR2(9)=>STRING
VARCHAR(9)=>STRING
NCHAR(9)=>STRING
NVARCHAR2(9)=>STRING
CLOB(9)=>STRING
NCLOB(9)=>STRING
NUMBER=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
NUMBER(9)=>INTEGER
NUMBER(9,0)=>INTEGER
NUMBER(9,2)=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
BINARY_FLOAT=>DOUBLE
BINARY_DOUBLE=>DOUBLE
DATE=>STRING
TIMESTAMP=>STRING
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE=>STRING
TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE=>STRING
BLOB=>null
RAW=>null
LONG RAW=>null
XMLTYPE=>STRING
PIG
int=>INTEGER
long=>INTEGER
float=>DOUBLE
double=>DOUBLE
chararray=>STRING
bytearray=>null
boolean=>BOOLEAN
datetime=>STRING
biginteger=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
bigdecimal=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
PostgreSQL
bigint=>INTEGER
bigserial=>INTEGER
int8=>INTEGER
bit=>BOOLEAN
bit(1)=>BOOLEAN
bit(32)=>INTEGER
bit varying=>BOOLEAN
bit varying(1)=>BOOLEAN
bit varying(32)=>INTEGER
varbit=>BOOLEAN
varbit(1)=>BOOLEAN
varbit(32)=>INTEGER
boolean=>BOOLEAN
bool=>BOOLEAN
bytea(9)=>null
character=>STRING
char=>STRING
date=>STRING
double precision=>DOUBLE
float8=>DOUBLE
integer=>INTEGER
int4=>INTEGER
json=>STRING
jsonb=>STRING
money=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
real=>DOUBLE
float4=>DOUBLE
smallint=>INTEGER
int2=>INTEGER
smallserial=>INTEGER
serial2=>INTEGER
serial=>INTEGER
serial4=>INTEGER
text=>STRING
time=>STRING
time without time zone=>STRING
time with time zone=>STRING
timestamp=>STRING
timestamp without time zone=>STRING
timestamp with time zone=>STRING
uuid=>STRING
xml=>STRING
SQL Server
bigint=>INTEGER
bit=>BOOLEAN
decimal=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
int=>INTEGER
money=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
numeric=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
numeric(9)=>INTEGER
numeric(9,0)=>INTEGER
numeric(9,2)=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
smallint=>INTEGER
smallmoney=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
tinyint=>INTEGER
float=>DOUBLE
real=>DOUBLE
date=>STRING
datetime2=>STRING
datetime=>STRING
datetimeoffset=>STRING
smalldatetime=>STRING
time=>STRING
char=>STRING
char(9)=>STRING
text=>STRING
varchar=>STRING
varchar(9)=>STRING
nchar=>STRING
nchar(9)=>STRING
ntext=>STRING
nvarchar=>STRING
nvarchar(9)=>STRING
binary=>null
image=>null
varbinary=>null
varbinary(9)=>null
cursor=>null
hierarchyid=>null
sql_variant=>null
table=>null
rowversion=>null
uniqueidentifier=>STRING
xml=>STRING
Teradata
Decimal=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
Byte(9)=>null
Blob(9)=>null
VarByte(9)=>null
Char(9)=>STRING
CLOB(9)=>STRING
Graphic(9)=>STRING
Char(9) Character Set Graphic=>STRING
JSON(9)=>STRING
VarChar(9)=>STRING
VarGraphic(9)=>STRING
VarChar(9) Character Set Graphic=>STRING
Date=>STRING
Time=>STRING
Time With Time Zone=>STRING
Timestamp=>STRING
Timestamp With Time Zone=>STRING
ByteInt=>INTEGER
BigInt=>INTEGER
Decimal=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
Decimal(9)=>INTEGER
Decimal(9,0)=>INTEGER
Decimal(9,2)=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
Double=>DOUBLE
Integer=>INTEGER
Number=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
Number(9)=>INTEGER
Number(9,0)=>INTEGER
Number(9,2)=>DOUBLE (DECIMAL if enabled)
SmallInt=>INTEGER
XML
float=>DOUBLE
decimal=>DOUBLE
double=>DOUBLE
unsignedLong=>INTEGER
unsignedInt=>INTEGER
unsignedShort=>INTEGER
unsignedByte=>INTEGER
positiveInteger=>INTEGER
negativeInteger=>INTEGER
nonPositiveInteger=>INTEGER
nonNegativeInteger=>INTEGER
long=>INTEGER
int=>INTEGER
integer=>INTEGER
byte=>INTEGER
short=>INTEGER
boolean=>BOOLEAN
anyURI=>STRING
language=>STRING
normalizedString=>STRING
token=>STRING
string=>STRING
duration=>STRING
gday=>STRING
gMonth=>STRING
gMonthDay=>STRING
gYear=>INTEGER
gYearMonth=>STRING
time=>STRING
Name=>STRING
NCName=>STRING
NOTATION=>STRING
QName=>STRING
ENTITY=>STRING
ENTITIES=>STRING
ID=>STRING
IDREF=>STRING
IDREFS=>STRING
NMTOKEN=>STRING
NMTOKENS=>STRING
anyType=>STRING
anySimpleType=>STRING
base64Binary=>STRING
hexBinary=>STRING
