A cross table is a common type of table featuring a matrix of values between two orthogonal lists of header data. It could look like the table below.
Example 1:
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun |
| 2008 | 45 | 65 | 78 | 12 | 78 | 22 |
| 2009 | 11 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 45 | 85 |
| 2010 | 65 | 56 | 22 | 79 | 12 | 56 |
| 2011 | 45 | 24 | 32 | 78 | 55 | 15 |
| 2012 | 45 | 56 | 35 | 78 | 68 | 82 |
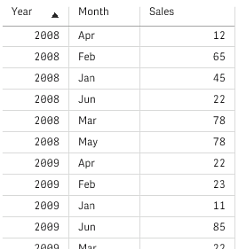
If this table is simply loaded into Qlik Sense, the result will be one field for Year and one field for each of the months. This is generally not what you would like to have. You would probably prefer to have three fields generated: one for each header category (Year and Month) and one for the data values inside the matrix.
This can be achieved by adding the crosstable prefix to the LOAD or SELECT statement, for example:
crosstable (Month, Sales) LOAD * from ex1.xlsx;
This creates the following result in Qlik Sense:
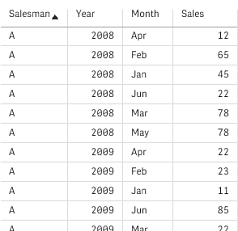
The cross table is often preceded by a number of qualifying columns, which should be read in a straightforward way. In this case there is one qualifying column, Year:
Example 2:
| Salesman | Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun |
| A | 2008 | 45 | 65 | 78 | 12 | 78 | 22 |
| A | 2009 | 11 | 23 | 22 | 22 | 45 | 85 |
| A | 2010 | 65 | 56 | 22 | 79 | 12 | 56 |
| A | 2011 | 45 | 24 | 32 | 78 | 55 | 15 |
| A | 2012 | 45 | 56 | 35 | 78 | 68 | 82 |
| B | 2008 | 57 | 77 | 90 | 24 | 90 | 34 |
| B | 2009 | 23 | 35 | 34 | 34 | 57 | 97 |
| B | 2010 | 77 | 68 | 34 | 91 | 24 | 68 |
| B | 2011 | 57 | 36 | 44 | 90 | 67 | 27 |
| B | 2012 | 57 | 68 | 47 | 90 | 80 | 94 |
In this case there are two qualifying columns to the left, followed by the matrix columns. The number of qualifying columns can be stated as a third parameter to the crosstable prefix as follows:
crosstable (Month, Sales, 2) LOAD * from ex2.xlsx;
This creates the following result in Qlik Sense: