This section describes a number of different ways you can load your data into the Qlik Sense app, depending on how the data is structured and which data model you want to achieve.
Turning data columns into rows
My data probably looks like this, and I want to have the sales figures in a separate field:
| Year | Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 34 | 54 | 53 | 52 |
| 2014 | 47 | 56 | 65 | 67 |
| 2015 | 57 | 56 | 63 | 71 |
Proposed action
Use the Crosstable prefix when you load the table.
The result will look like this:
| Year | Quarter | Sales |
|---|---|---|
| 2013 | Q1 | 34 |
| 2013 | Q2 | 54 |
| 2013 | Q3 | 53 |
| 2013 | Q4 | 52 |
| 2014 | Q1 | 47 |
| ... | ... | ... |
To learn more about crosstables, see Working with crosstables in the data load script and Crosstable.
Turning data rows into fields
I have a generic table with three fields similar to this, and I want to have each attribute as a separate table:
| Object | Attribute | Value |
|---|---|---|
| ball | color | red |
| ball | diameter | 25 |
| ball | weight | 3 |
| box | color | 56 |
| box | height | 30 |
| box | length | 20 |
| box | width | 25 |
Proposed action
Create a generic data model using the Generic load prefix.
You will get a data model that looks like this:
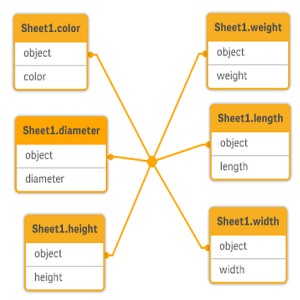
To learn more about generic data, see Generic databases and Generic.
Loading data that is organized in hierarchical levels, for example an organization scheme
My data is stored in an adjacent nodes table that looks like this:
| NodeID | ParentNodeID | Title |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | General manager |
| 2 | 1 | Country manager |
| 3 | 2 | Region manager |
Proposed action
Load the data with the Hierarchy prefix to create an expanded nodes table:
| NodeID | ParentNodeID | Title | Level1 | Level2 | Level3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | General manager | General manager | - | - |
| 2 | 1 | Country manager | General manager | Country manager | - |
| 3 | 2 | Region manager | General manager | Country manager | Region manager |
To learn more about hierarchical levels, see Loading hierarchy data and Hierarchy.
Loading only new or updated records from a large database
I have a database with a large number of records, and I don't want to reload the entire database to refresh the data in my app. I only want to load new or updated records, and remove records that are deleted from the database.
Proposed action
Implement an incremental load solution using QVD files.
For more information, see Loading new and updated records with incremental load.
Combining data from two tables with a common field
Qlik Sense will associate tables with a common field automatically, but I want to control how the tables are combined.
Proposed action : Join / Keep
You can combine two tables into a single internal table with the Join or Keep prefixes.
For more information, see Combining tables with Join and Keep.
Proposed action : Mapping
An alternative to joining tables is to use mapping, which automates lookup of associated values in a mapping table. This can reduce the amount of data to load.
For more information, see Using mapping as an alternative to joining.
Matching a discrete value to an interval
I have a table of discrete numeric values (Event), and I want to match it to one or more intervals (Start and End).
| Time | Event | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| 00:00 | 0 | Start of shift 1 |
| 01:18 | 1 | Line stop |
| 02:23 | 2 | Line restart 50% |
| 04:15 | 3 | Line speed 100% |
| 08:00 | 4 | Start of shift 2 |
| 11:43 | 5 | End or production |
| Start | End | Order |
|---|---|---|
| 01:00 | 03:35 | A |
| 02:30 | 07:58 | B |
| 03:04 | 10:27 | C |
| 07:23 | 11:43 | D |
Proposed action
Use the IntervalMatch prefix to link the Time field with the interval defined by Start and End.
For more information, see Matching intervals to discrete data.
If the interval is not defined explicitly with start and end, only with a change timestamp like in the table below, you need to create an interval table.
| Currency | Change Data | Rate |
|---|---|---|
| EUR | - | 8.59 |
| EUR | 28/01/2013 | 8.69 |
| EUR | 15/02/2013 | 8.45 |
| USD | - | 6.50 |
| USD | 10/01/2013 | 6.56 |
| USD | 03/02/2013 | 6.30 |
For more information, see Creating a date interval from a single date.
Handling inconsistent field values
My data contains field values that are not consistently named in different tables. For example, one table contains the value US in Country while another table contains United States. This situation will prevent associations.
| Country | Region |
|---|---|
| US | Maryland |
| US | Idaho |
| US | New York |
| US | California |
| Country | Population |
|---|---|
| United States | 304 |
| Japan | 128 |
| Brazil | 192 |
| China | 1333 |
Proposed action
Perform data cleansing using a mapping table, that will compare field values and enable correct associations.
For more information, see Data cleansing.
Handling inconsistent field value capitalization
My data contains field values that are not consistently formatted in different tables. For example, one table contains the value single in Type while another table contains Single in the same field. This situation will prevent associations, as the Type field will contain both single and Single values, capitalization matters.
| Type | Price |
|---|---|
| single | 23 |
| double | 39 |
| Type | Color |
|---|---|
| Single | Red |
| Single | Blue |
| Double | White |
| Double | Black |
Proposed action
If you loaded the data with Add data, you can fix this in the data manager.
Do the following:
- In the data manager, open Table2 in the table editor.
-
Rename the Type field to Table2.Type.
If you just added the table with Add data with data profiling enabled, the field may already be named Table2.Type to prevent automatic association. In this case, this procedure will associate the two tables.
- Create a calculated field using the expression Lower(Table2.Type) and name it Type.
- Click Load data.
Table1 and Table2 should now be associated by the field Type, which only contains values in lowercase, like single and double.
If you want to use different capitalization, you can also achieve this with similar procedures, but remember that the tables will associate using the fields with the same name.
- To get all values capitalized, like Single, create the calculated Type field in Table1 instead, and use the expression Capitalize(Table1.Type).
- To get all values in uppercase, like SINGLE, create the calculated Type field in both tables, and use the expressions Upper(Table1.Type) and Upper(Table2.Type) respectively.
To learn more about calculated fields, see Using calculated fields.
To learn more about capitalization, see Capitalize - script and chart function, Lower - script and chart function and Upper - script and chart function.
Loading geospatial data to visualize data with a map
I have data that I want to visualize using a map, for example sales data per country, or per store. To use the map visualization I need to load area or point data.
Proposed action
You can load area or point data that match your data value locations from a KML file or an Excel file. Additionally, you need to load the actual map background.
For more information, see Loading your own map data.
